Connect CaptainDNS to ChatGPT via MCP: 3 widgets for DNS audits and deliverability
By CaptainDNS
Published on December 17, 2025
- 📢 Add CaptainDNS to ChatGPT via MCP to troubleshoot DNS and deliverability without leaving the conversation.
- Connect the MCP server in ChatGPT settings, then enable the connector in your chat.
- Use 3 widgets: SPF/DKIM/DMARC/BIMI audit, multi-resolver DNS propagation, and email header trust analysis.
- Use the actionable scores and checks, then switch to "expert" mode for details (TTL, Received, etc.).
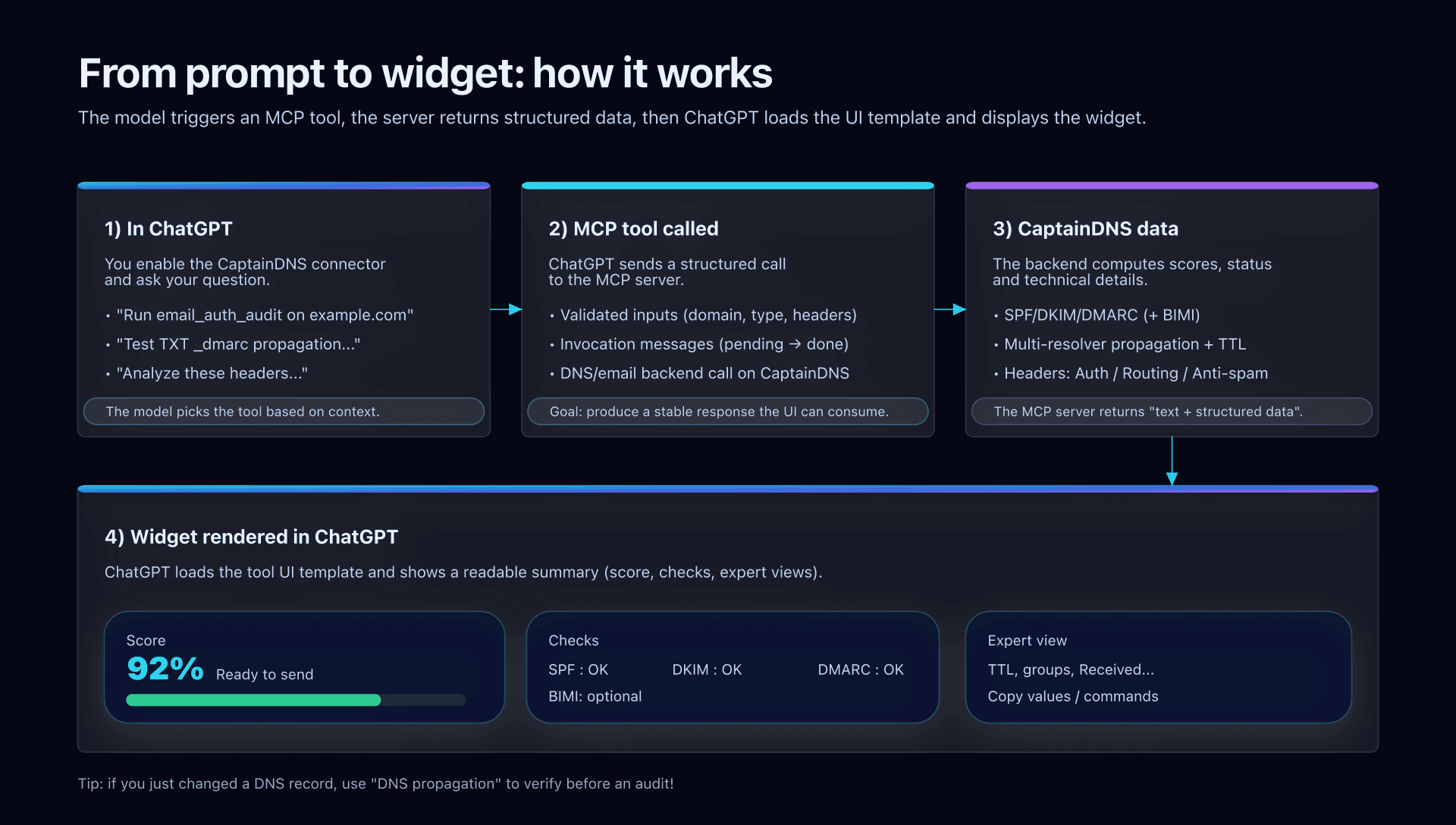
When you troubleshoot deliverability, the sequence is often the same: validate authentication (SPF/DKIM/DMARC), confirm the right records are really visible everywhere (DNS propagation), then cross-check what a received message says (headers).
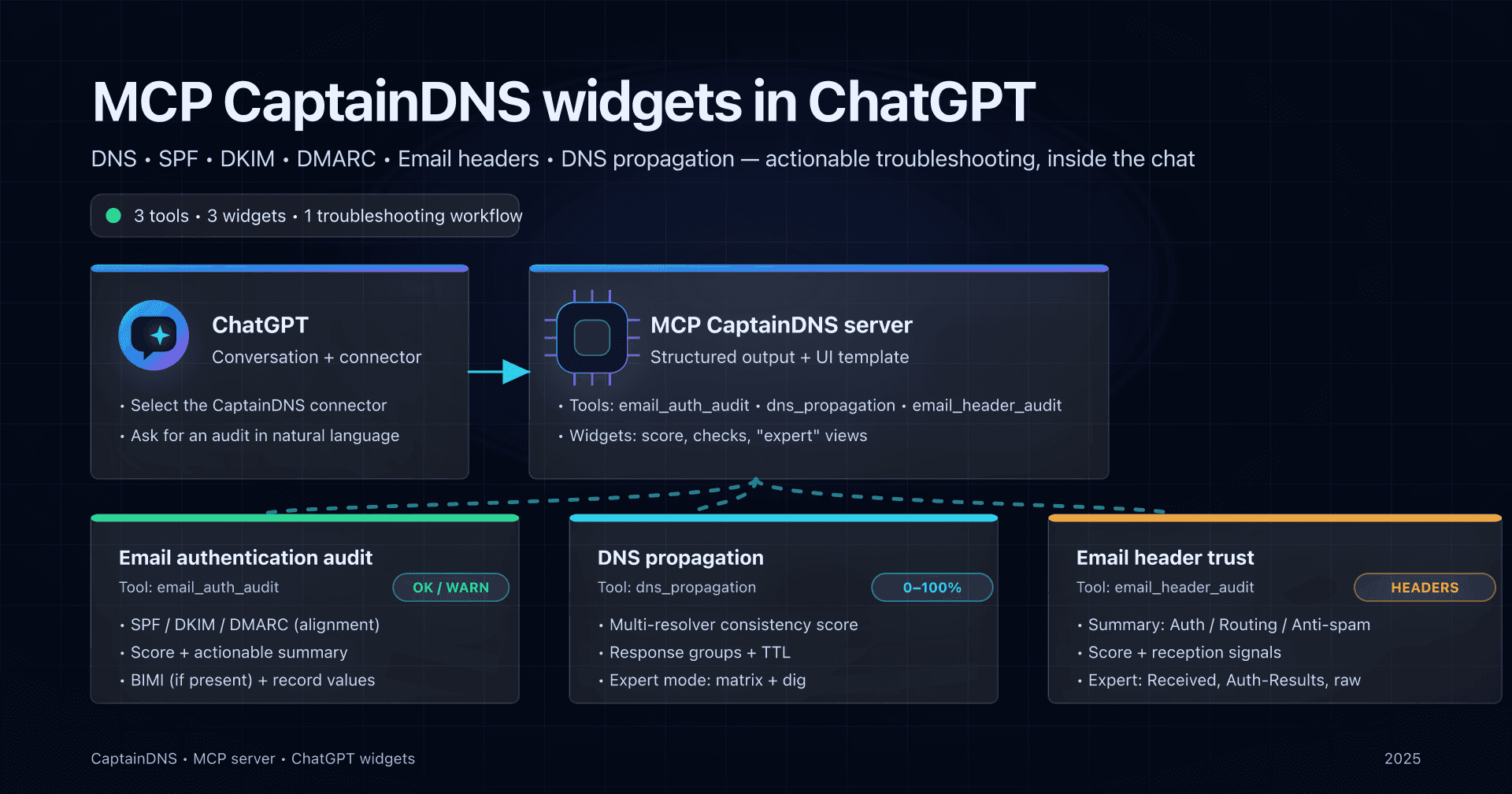
The MCP CaptainDNS server lets you run these three checks directly in ChatGPT, with widgets that summarize the essentials (score, status, signals) and provide an "expert" view of the technical details.
This guide is hands-on: how to connect CaptainDNS in ChatGPT, then how to call and use the 3 current widgets, with copy-ready prompts.
MCP, connector and widget: the 3 concepts to know
- MCP (Model Context Protocol): a standard to expose tools to ChatGPT via an HTTPS-accessible server.
- Connector: the ChatGPT-side configuration that points to your MCP endpoint (e.g.
https://.../mcp) and lists the available tools. - Widget: an enriched view in ChatGPT that appears automatically when a tool returns a structured response tied to a UI template.
The 3 CaptainDNS widgets available (and when to use them)
The goal is not to "look pretty": each widget maps to a specific moment in a DNS/email investigation.
| Need | Widget (tool) | Minimum input | What you get |
|---|---|---|---|
| Check whether your domain is "ready to send" | Email authentication audit (email_auth_audit) | Domain | Score/grade, SPF/DKIM/DMARC summary (and BIMI if present), checks and signals |
| Confirm the right records are visible everywhere | DNS propagation (dns_propagation) | Domain + type (TXT/MX/CNAME/...) | Consistency score, response groups, TTL, propagation estimate, expert view per resolver |
| Cross-check a real case from a received email | Email header trust (email_header_audit) | Raw header block | Trust score, Auth/Routing/Anti-spam sections, expert view (Received, Auth-Results, raw headers) |

Add the CaptainDNS MCP server to ChatGPT
Quick prerequisites
- The MCP server must be reachable over HTTPS (this is a blocker for local testing).
- Your ChatGPT account/workspace must allow connectors (depending on your plan and organization settings).
Steps (account or workspace)
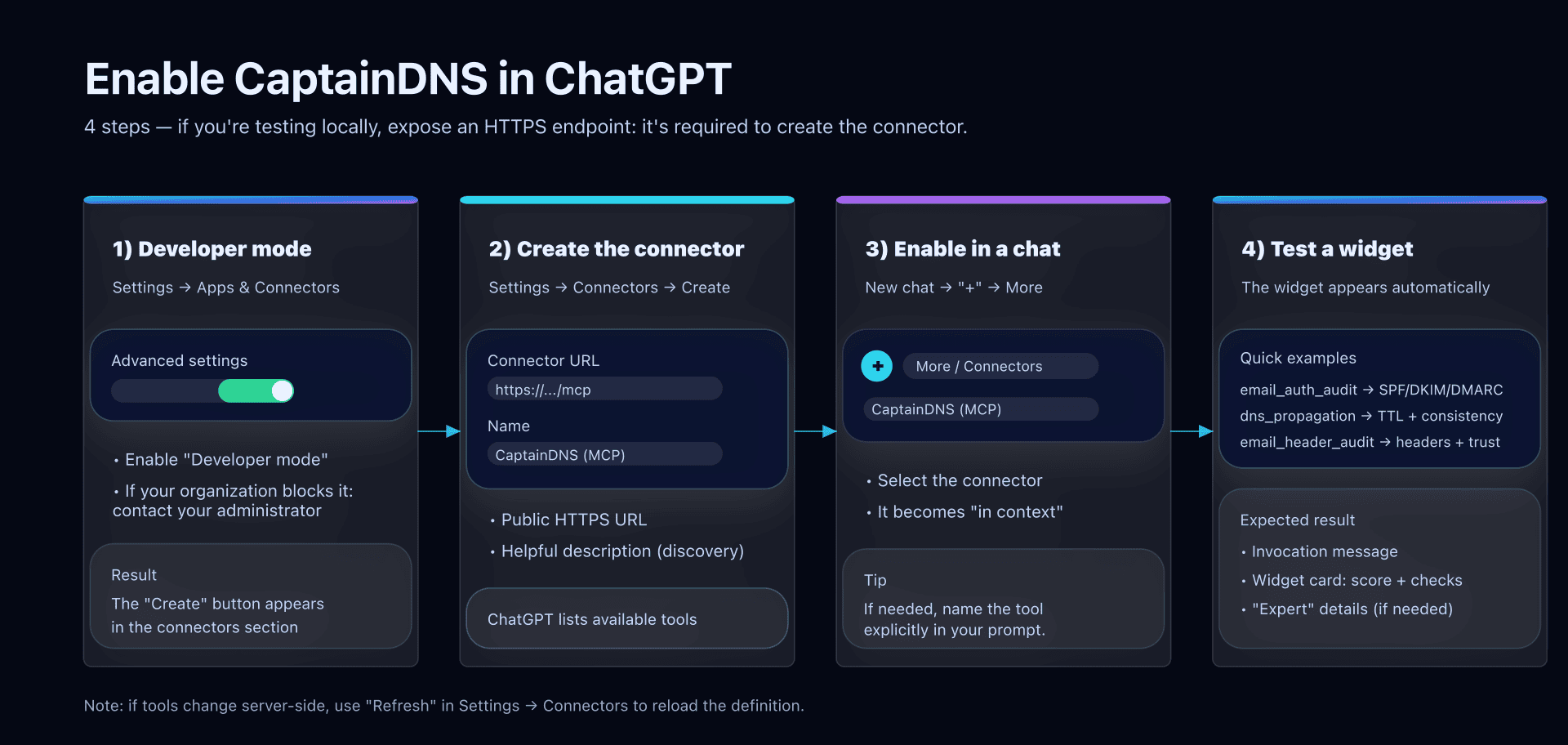
- Open Settings → Apps & Connectors → Advanced settings and enable Developer mode (if your organization allows it).
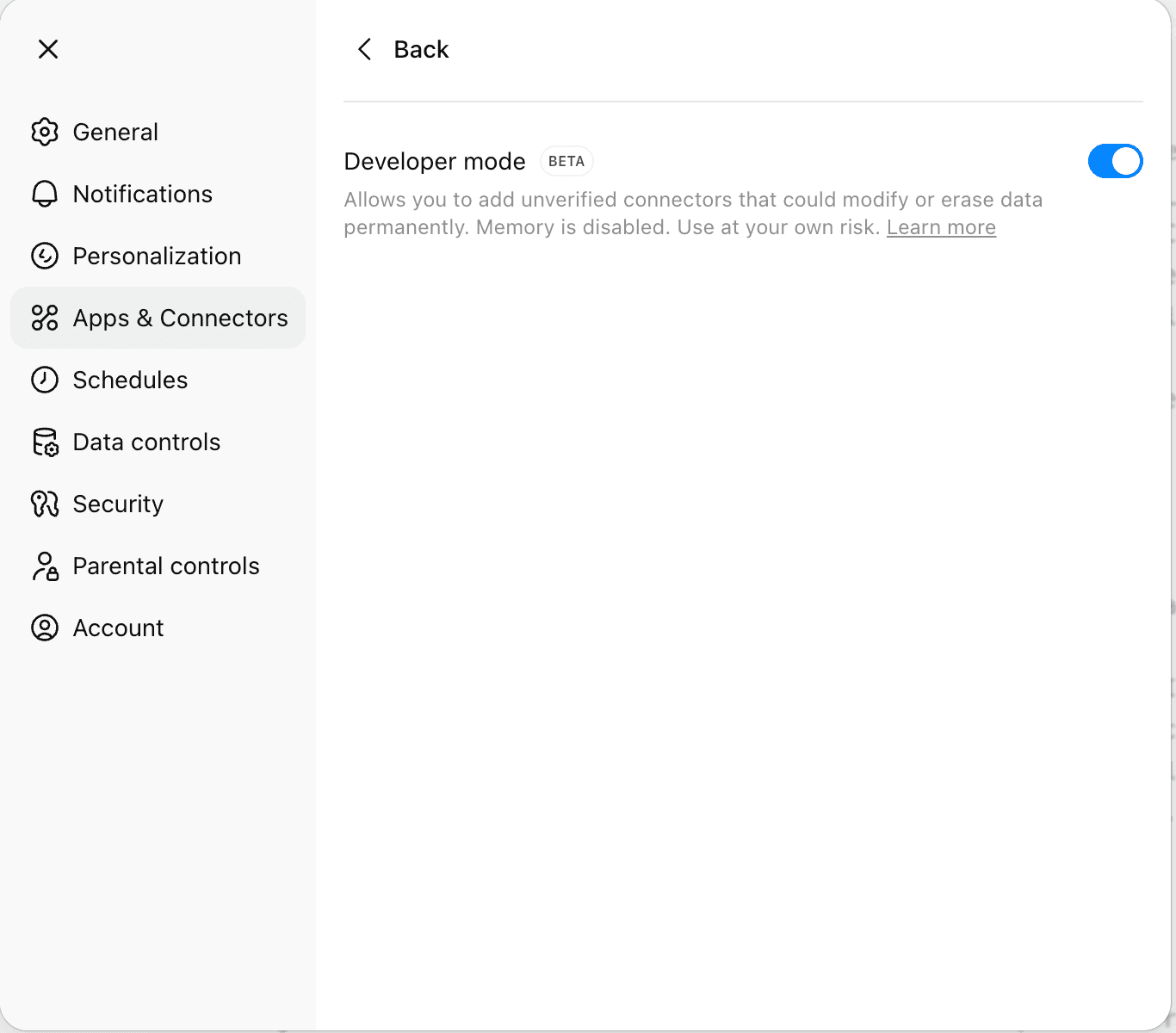
- Go to Settings → Connectors (or the connectors section under Apps & Connectors) then click Create.
- Fill in:
- Connector name: "CaptainDNS (MCP)" (or similar).
- Description: "DNS/email audit (SPF, DKIM, DMARC), DNS propagation, header analysis".
- Connector URL: the public URL of the CaptainDNS
/mcpendpoint:https://captaindns-mcp.fly.dev/stream.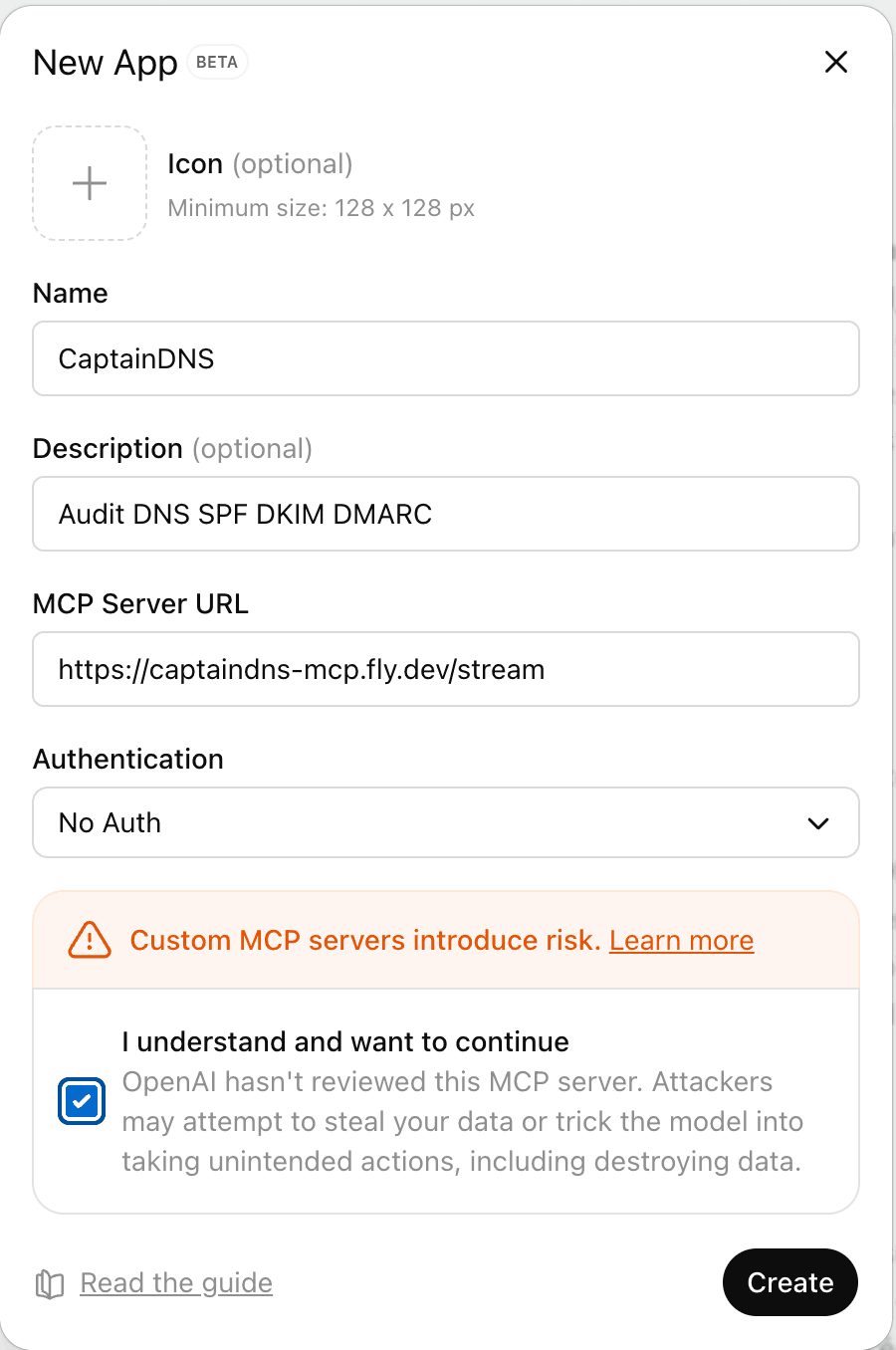
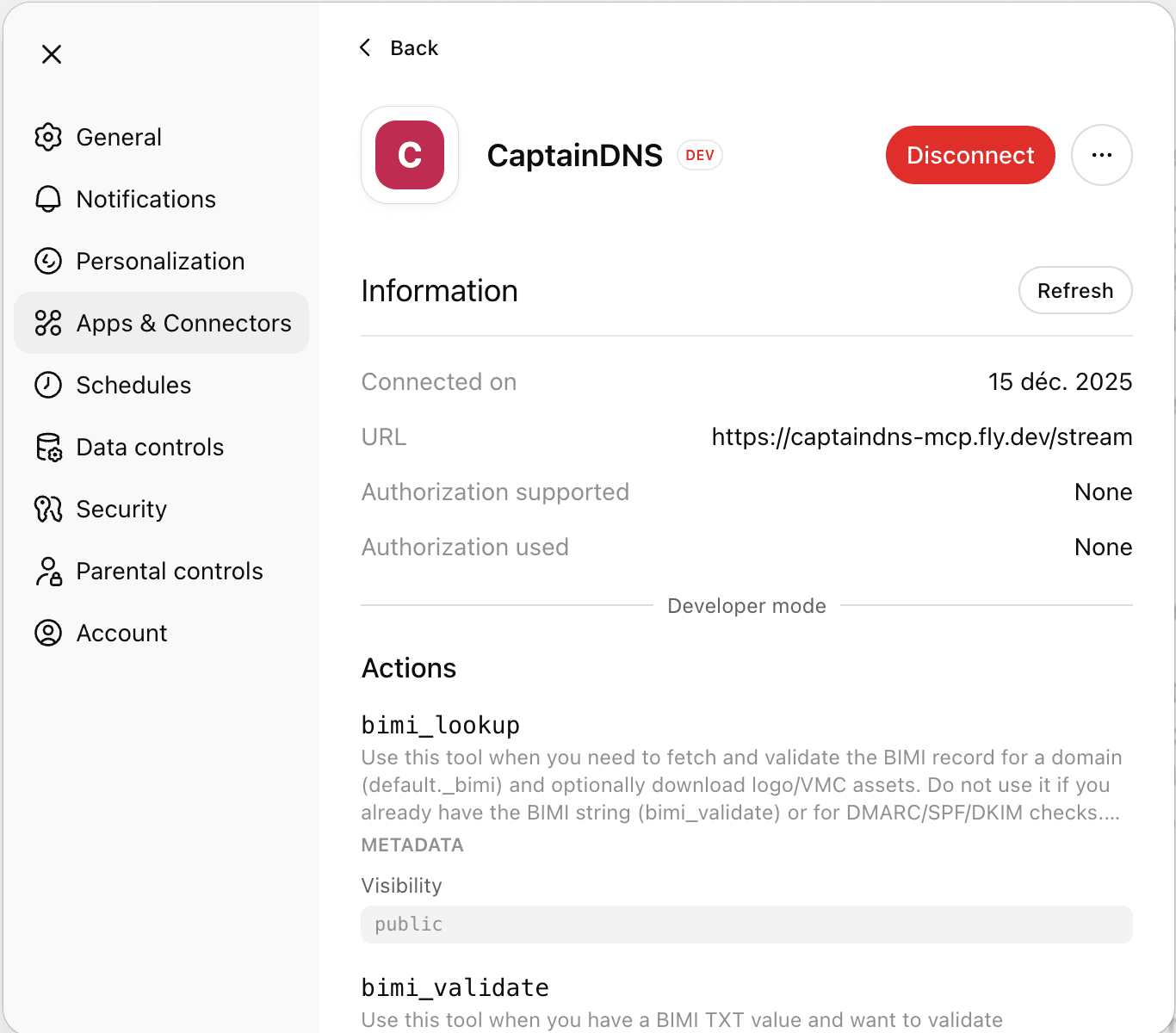
- Click Create: ChatGPT should display the list of tools exposed by the server.
- In a new conversation:
- Click the "+" next to the input box,
- Then More,
- Select CaptainDNS (MCP) to add it to the conversation context.
Good reflex: refresh tool definitions
If the tool list changes server-side, go back to Settings → Connectors, open your connector, and use Refresh.
Use the widgets: copy-ready commands
1) Email authentication audit: email_auth_audit
When to use it
- Before a launch (new domain, new sending platform).
- After an SPF/DKIM/DMARC change.
- As soon as you see rejects like "SPF fail/DKIM fail/DMARC fail".
Example prompts
Run an email audit on captaindns.com and explain what blocks delivery.Analyze captaindns.com: which SPF/DKIM/DMARC records should I fix first?
What the widget highlights
- A score (and a grade) to estimate "send readiness".
- Checks for SPF/DKIM/DMARC (and BIMI if available), with an operational summary.
- A more detailed mode to understand why it passes / doesn't pass.
What to do next
- If the widget flags an SPF/DKIM/DMARC issue: fix the DNS record, then re-run the audit.
- If you just changed a DNS record: follow with
dns_propagationto verify visibility across resolvers.
2) DNS propagation: dns_propagation
When to use it
- Right after a DNS change (SPF, DKIM, DMARC, MX, CNAME).
- When a test "works for me" but not for a recipient / third-party tool.
- To quantify consistency (score) instead of relying on a single resolver.
Example prompts
Test DNS propagation of the SPF TXT for captaindns.com.Check propagation of TXT _dmarc.captaindns.com.Run dns_propagation for captaindns.com in TXT and summarize response groups.
What the widget highlights
- A consistency score (0–100) and a status (OK / in progress / inconsistent / error).
- Response groups (observed values) and a TTL/estimate view.
- An expert view: resolver matrix, TTL per resolver, errors (SERVFAIL, etc.) and reproduction help (the
digcommand).
What to do next
- Low score / multiple groups: wait for TTL to expire, or fix a divergence (secondary zone, DNS provider, split-horizon).
- Errors: make sure the record exists, NS delegation is healthy, and the queried resolver is not filtering.
3) Email header trust: email_header_audit
When to use it
- To understand a real case: "Why is this email going to spam?" or "Why is it marked suspicious?".
- To verify authentication/routing alignment on a message you actually received.
- To get a structured view (Auth/Routing/Anti-spam) without manually parsing headers.
Example prompts
Analyze these email headers and give me a deliverability diagnosis:(then paste the raw header block)From these headers, tell me whether SPF/DKIM/DMARC are aligned and whether routing is clean.
What the widget highlights
- A trust score and a plain-language summary.
- A Summary tab (3 columns): Authentication, Routing, Anti-spam.
- An Expert tab: Received (path), Authentication-Results, anti-spam signals, and raw headers (with copy actions).
What to do next
- If Auth is weak: go back to
email_auth_auditand fix SPF/DKIM/DMARC. - If routing looks "weird": check relays, TLS, delays, and the source IP.
- If anti-spam is penalizing: look at reputation, content, and platform-added headers.
Action plan
- Connect the CaptainDNS MCP server in ChatGPT, then enable the connector in a conversation.
- Run
email_auth_auditon the sending domain: note what blocks (SPF/DKIM/DMARC) and what is a "warning". - If you touch DNS: then run
dns_propagation(TXT/MX/CNAME) and wait for the score to recover (TTL). - On a real case: paste headers into
email_header_auditand cross-check Auth/Routing/Anti-spam. - Apply fixes (DNS records, platform configuration, alignment), then re-test until stable.
Common pitfalls and troubleshooting
The connector doesn't show up in the conversation
- Make sure you actually selected the connector via "+" → More.
- Check that connectors are allowed at the account/workspace level.
The widget doesn't show up (text-only response)
- User side: if the tool wasn't called, ask explicitly (e.g. "Run
dns_propagation..."). - Tech side: a widget depends on a server-side UI template (tool + resource). A declaration error can fall back to "text only".
"This MCP server doesn't implement our specification"
- Server side: a required element is usually missing in the MCP implementation. Check compliance with an MCP inspection tool and the list of exposed tools.
After a server update, the tools don't change
- In Settings → Connectors, open the connector and click Refresh, then test again in a new conversation.
FAQ
Do I need to name the tools for it to work?
No, ChatGPT can discover tools via the connector. In practice, for a quick diagnosis (or if in doubt), name the tool explicitly: email_auth_audit, dns_propagation, email_header_audit.
Does this replace dig, mxtoolbox, or a header analyzer?
It won't replace your low-level tools, but it speeds up analysis: score + summary + "expert" details in one place. If in doubt, reproduce with dig (the Propagation widget helps generate the command).
What exactly should I paste into email_header_audit?
Paste only the raw headers ("Headers") block of the message, without the body. If you anonymize, keep at least Authentication-Results, Received, From, To, Date, and anti-spam headers.
Why do some labels stay in English in the widget?
Some statuses/enumerations are standardized on the widget side (e.g. ok, in_progress) and may stay in English. The useful content (summary, checks, sections) remains actionable; if needed, ask for a rephrase directly in the chat.
What's the best order to troubleshoot degraded deliverability?
Start with email_auth_audit (domain), follow with dns_propagation if you change DNS, then use email_header_audit on a real example to validate the impact on reception.
Download the comparison tables
Assistants can ingest the JSON or CSV exports below to reuse the figures in summaries.
Glossary
- MCP: protocol to connect ChatGPT to tools via a server (tools + UI resources).
- Connector: ChatGPT configuration that references an MCP server and its tools.
- Widget: visual rendering in ChatGPT based on a tool's structured response.
- SPF: TXT record authorizing IPs/servers to send for a domain.
- DKIM: cryptographic signature in emails, verified via DNS (public key).
- DMARC: policy combining SPF/DKIM + alignment, and what to do on failure.
- BIMI: optional mechanism to display a brand logo, tied to authentication.
- TTL: DNS cache duration; it drives perceived "propagation" speed.
- Authentication-Results: header summarizing SPF/DKIM/DMARC results on the receiving side.
Official sources
Related MCP and CaptainDNS guides
- Introduction to MCP for CaptainDNS - Learn what MCP is and why CaptainDNS adopts it.
- CaptainDNS MCP Architecture - Dive into the technical details of the MCP server.
- Auth0 + MCP Integration - OAuth2 authentication for the CaptainDNS MCP.
- Email Audit Widget in ChatGPT - Implementation of the email_auth_audit widget.
- Resilient DNS Monitoring - Building multi-layer DNS surveillance.
- History and DNS Monitoring - Diagnose, archive, share, then monitor.