Why Your Emails End Up in Spam: The Complete Diagnostic Guide
By CaptainDNS
Published on February 4, 2026
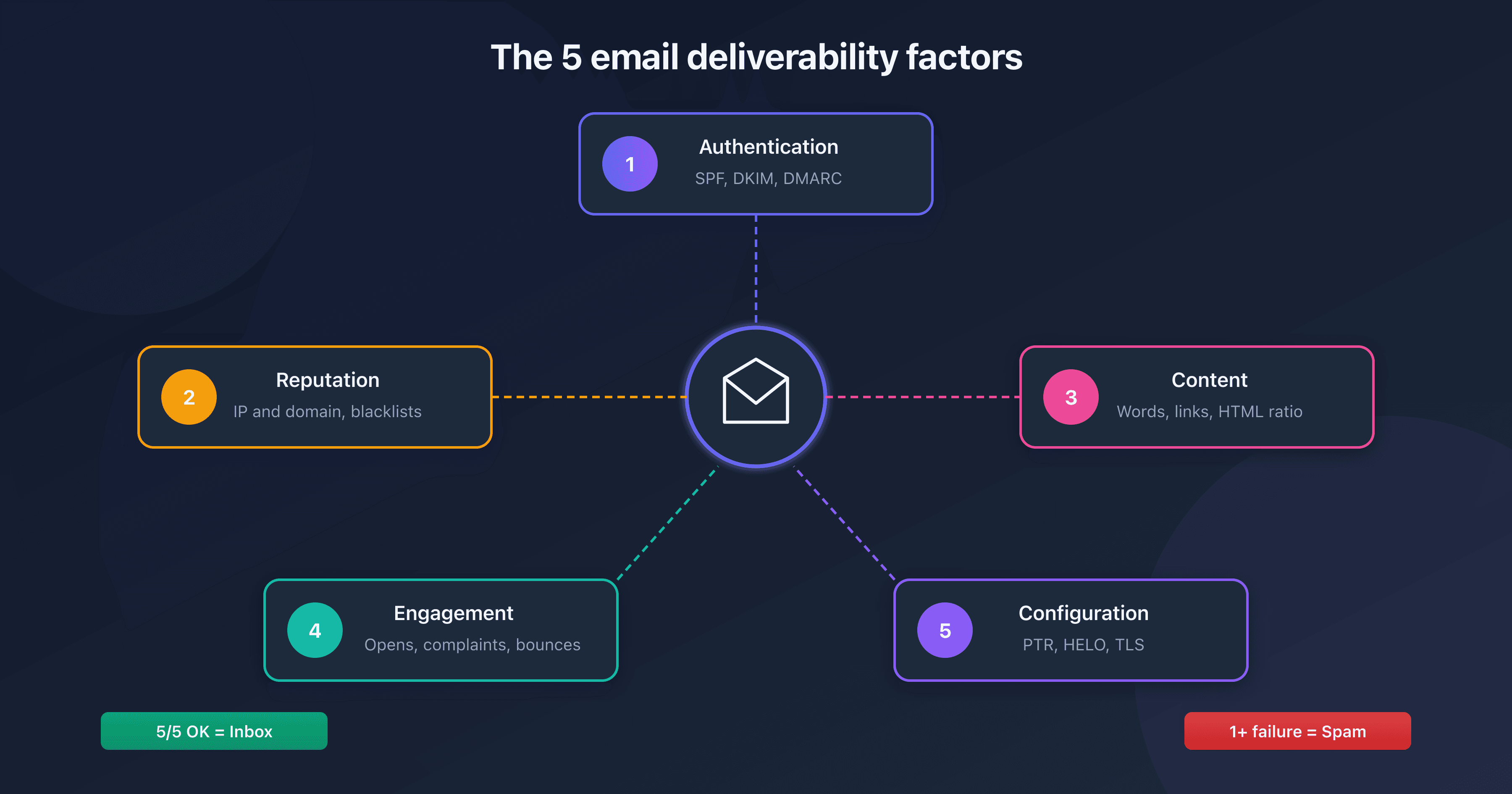
- 5 main causes: authentication (SPF/DKIM/DMARC), IP/domain reputation, suspicious content, poor engagement, technical configuration
- Priority check: test your IP against major blocklists and audit your authentication
- Since 2024: Gmail and Yahoo require SPF, DKIM, and DMARC for bulk senders
- Critical threshold: a complaint rate above 0.1% triggers spam classification
- Quick diagnostic: analyze your email headers to identify the exact problem
Why Your Emails Are Being Classified as Spam
Every day, billions of emails are filtered by anti-spam systems. One in six emails never reaches the recipient's inbox. For businesses, this is a critical issue: invoices not received, order confirmations lost, customer communications ignored.
Spam classification isn't random. Email providers (Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo) use hundreds of signals to decide the fate of each email. Understanding these signals is key to solving the problem.
This guide analyzes the 5 main causes of spam classification and gives you a concrete action plan for each situation. Whether you're a system administrator, marketing manager, or developer, you'll find the answers you need.
Cause 1: Missing or Incorrect Email Authentication
Email authentication became mandatory in 2024. Gmail, Yahoo, and Apple announced that unauthenticated emails would be systematically rejected or classified as spam.
The 3 Authentication Protocols
| Protocol | Function | Impact if Missing |
|---|---|---|
| SPF | Lists servers authorized to send for your domain | Rejection or spam |
| DKIM | Cryptographically signs each email | Spam or distrust |
| DMARC | Defines the policy when SPF/DKIM fails | No protection against spoofing |
Check Your Configuration
Use a domain email audit to instantly verify if your domain is properly configured:
- Enter your domain name
- Review the SPF, DKIM, and DMARC results
- Follow the correction recommendations
Common SPF Errors
| Error | Consequence | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No SPF record | Emails classified as spam | Create a TXT record with v=spf1 |
| Too many includes (>10 lookups) | Invalid SPF (PermError) | Optimize or use a flattening service |
| Missing IP | SPF failure for some sends | Add the IP or the service's include |
| ~all vs -all | Policy too permissive | Use -all in production |
Common DKIM Errors
| Error | Consequence | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No signature | Email not authenticated | Configure DKIM on the mail server |
| Key too short (<1024 bits) | Signature considered weak | Generate a 2048-bit key |
| Incorrect selector | Verification failure | Check DNS and server configuration |
| Modified body | Invalid signature | Check intermediate relays |
DMARC: The Game-Changing Policy
DMARC is the conductor of authentication. Without it, even with valid SPF and DKIM, your emails can be classified as spam.
# Minimal DMARC record
_dmarc.captaindns.com TXT "v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc@captaindns.com"
# Strict DMARC record (recommended for production)
_dmarc.captaindns.com TXT "v=DMARC1; p=reject; rua=mailto:dmarc@captaindns.com; pct=100"
| Policy | Behavior | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
p=none | Monitoring only | Initial phase (2-4 weeks) |
p=quarantine | Suspicious emails to spam | Intermediate phase |
p=reject | Suspicious emails rejected | Secure production |
Cause 2: Degraded IP or Domain Reputation
Even with perfect authentication, your emails can land in spam if your reputation is poor. Email providers maintain reputation scores based on sending history.
Understanding Reputation
Reputation consists of two elements:
- IP reputation: Score of the IP address sending the emails
- Domain reputation: Score of the sending domain (From)
| Factor | Impact on Reputation |
|---|---|
| Spam complaint rate | Very high (threshold: 0.1%) |
| Bounce rate | High (threshold: 5%) |
| Engagement (opens, clicks) | Moderate |
| Domain history | Moderate |
| Blocklists | Critical |
Check If Your IP Is Blocklisted
An IP on a major blocklist (Spamhaus, Barracuda) will see its emails systematically rejected by Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo.
To check if your IP is listed, test it against the main DNSBLs:
- Spamhaus ZEN: Used by the majority of major providers
- Barracuda BRBL: Very common in enterprise environments
- SpamCop: Based on user reports
Priority Blocklists to Monitor
| Blocklist | Impact | Used By |
|---|---|---|
| Spamhaus ZEN | Critical | Gmail, Yahoo, Outlook |
| Barracuda BRBL | Critical | Enterprises, Barracuda filters |
| SpamCop | High | Many providers |
| SORBS | Moderate | Anti-spam filters |
Improving Your Reputation
| Action | Impact | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Request delisting from blocklists | Immediate | 24-72h |
| Reduce complaint rate | High | 2-4 weeks |
| Clean lists (hard bounces) | High | Immediate |
| Gradually warm up new IPs | Preventive | 4-6 weeks |
Cause 3: Problematic Content
Anti-spam filters analyze the content of each email. Certain elements automatically trigger spam classification.
Words and Phrases to Avoid
Anti-spam filters use lists of suspicious words. Here are the riskiest categories:
| Category | Examples | Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Excessive urgency | "URGENT", "Act now", "Last chance" | High |
| Financial promises | "Free", "Make money", "No cost" | High |
| Sales pressure | "Limited offer", "Only 24h left", "Out of stock" | Moderate |
| Suspicious phrases | "Click here", "100% guaranteed", "No obligation" | Moderate |
Email Structure
| Problem | Why It's Filtered | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| 100% image email | Hidden text, spammer technique | 60% text / 40% images ratio |
| Shortened links (bit.ly) | Mask destination | Use full URLs |
| Too many links | Typical spam behavior | Maximum 3-5 links per email |
| No text version | HTML only = suspicious | Always include text/plain |
| Embedded forms | Phishing technique | Link to website |
Optimal HTML/Text Ratio
Recommended content:
- Text: 60-80%
- Images: 20-40%
- Links: 3-5 maximum
- Total size: < 100 KB
Cause 4: Poor Recipient Engagement
Email providers measure how recipients interact with your emails. Low engagement signals unwanted content.
Negative Engagement Signals
| Signal | Impact | Critical Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Spam complaints | Very high | >0.1% triggers spam |
| Hard bounces | High | >5% degrades reputation |
| Repeated soft bounces | Moderate | >10% over 30 days |
| Low open rate | Moderate | <10% on active lists |
| High unsubscribes | Moderate | >1% per campaign |
The Spam Vicious Cycle
Low engagement → Spam classification → Even less engagement → Degraded reputation
To break this cycle:
- Clean your lists: Remove addresses inactive for more than 6 months
- Segment: Send relevant content to each segment
- Respect consent: Double opt-in required
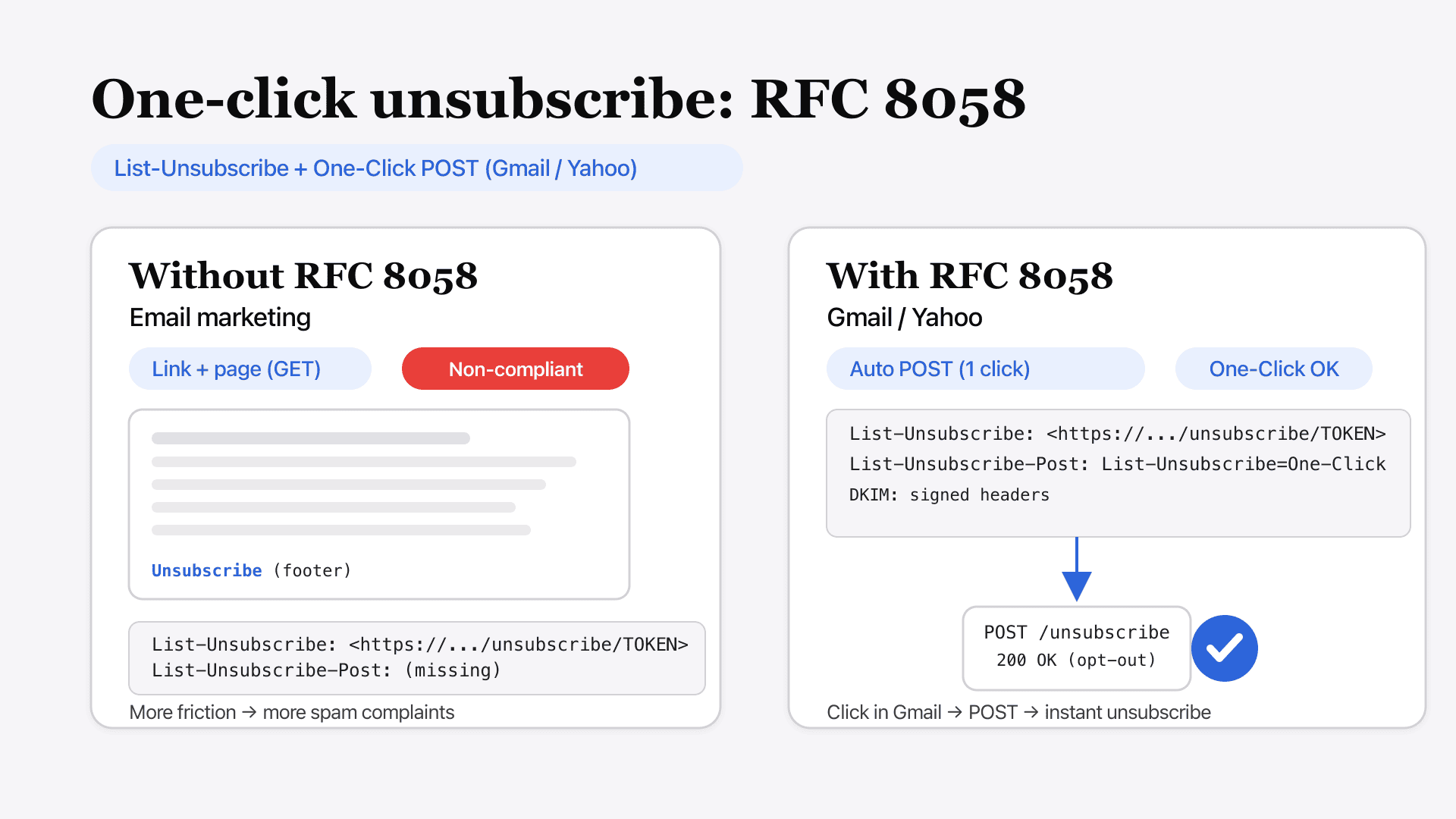
- Make unsubscribing easy: Visible link, 1-click process
List Hygiene Best Practices
| Action | Frequency | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Remove hard bounces | Immediate | Critical |
| Remove spam complaints | Immediate | Critical |
| Clean inactive (>6 months) | Monthly | High |
| Re-engage lukewarm contacts | Quarterly | Moderate |
| Validate emails at signup | Ongoing | Preventive |
Cause 5: Poor Technical Configuration
Technical configuration issues can sabotage all your efforts.
Server Configuration Checklist
| Element | Verification | Command |
|---|---|---|
| Reverse DNS (PTR) | IP must resolve to an FQDN | dig -x <IP> |
| FQDN to IP | FQDN must resolve to the IP | dig A <fqdn> |
| HELO/EHLO | Must match the PTR | Server logs |
| Port 25 open | No ISP blocking | telnet mail.server.com 25 |
| TLS enabled | STARTTLS required | Connection test |
Reverse DNS: Why It's Critical
Reverse DNS (PTR record) is checked by all major providers. Without a valid PTR, your emails are immediately suspicious.
# Check your IP's PTR
dig -x 192.0.2.1
# Expected result
1.2.0.192.in-addr.arpa. 3600 IN PTR mail.captaindns.com.
# The FQDN must resolve to the same IP
dig A mail.captaindns.com
# Result: 192.0.2.1
HELO/EHLO Configuration
The mail server identifies itself with HELO or EHLO. This identification must:
- Be a valid FQDN (not an IP, not "localhost")
- Resolve to the IP sending the email
- Match the PTR of that IP
# Bad
EHLO localhost
EHLO [192.0.2.1]
EHLO server1
# Good
EHLO mail.captaindns.com
Diagnosis by Provider
Each provider has its own specifics. Here's how to diagnose problems for the main ones.
Gmail
Diagnostic tools:
- Google Postmaster Tools: domain and IP reputation
- Gmail headers: look for
X-Gm-SpamandX-Gm-Phishy
Gmail 2024 Requirements:
| Criterion | Volume <5000/day | Volume >5000/day |
|---|---|---|
| SPF or DKIM | Required | Required |
| DMARC | Recommended | Required |
| Complaint rate | <0.3% | <0.1% |
| TLS | Recommended | Required |
| 1-click unsubscribe | - | Required |
Common error codes:
| Code | Meaning | Action |
|---|---|---|
421 4.7.0 | Too many connections | Reduce rate |
550 5.7.1 | DMARC policy | Fix SPF/DKIM |
550 5.7.26 | Authentication failure | Check SPF, DKIM |
Outlook / Microsoft 365
Diagnostic tools:
- SNDS (Smart Network Data Services): IP reputation
- JMRP: feedback loop
Outlook specifics:
- Uses Spamhaus and proprietary blocklists
- Aggressive filtering of new domains (<30 days)
- SNDS program to monitor reputation
Common error codes:
| Code | Meaning | Action |
|---|---|---|
550 5.7.1 | IP blocked | Request delisting at sender.office.com |
550 5.7.606 | Low reputation IP | SNDS + list cleanup |
421 4.7.0 | Rate limit | Reduce sends |
Yahoo / AOL
Diagnostic tools:
- Yahoo Sender Hub: reputation and guidelines
- Complaint Feedback Loop: real-time complaints
Yahoo 2024 Requirements:
| Criterion | Required |
|---|---|
| SPF | Required |
| DKIM | Required |
| DMARC | Required for >5000 emails/day |
| 1-click unsubscribe | Required |
| Complaint rate | <0.3% |
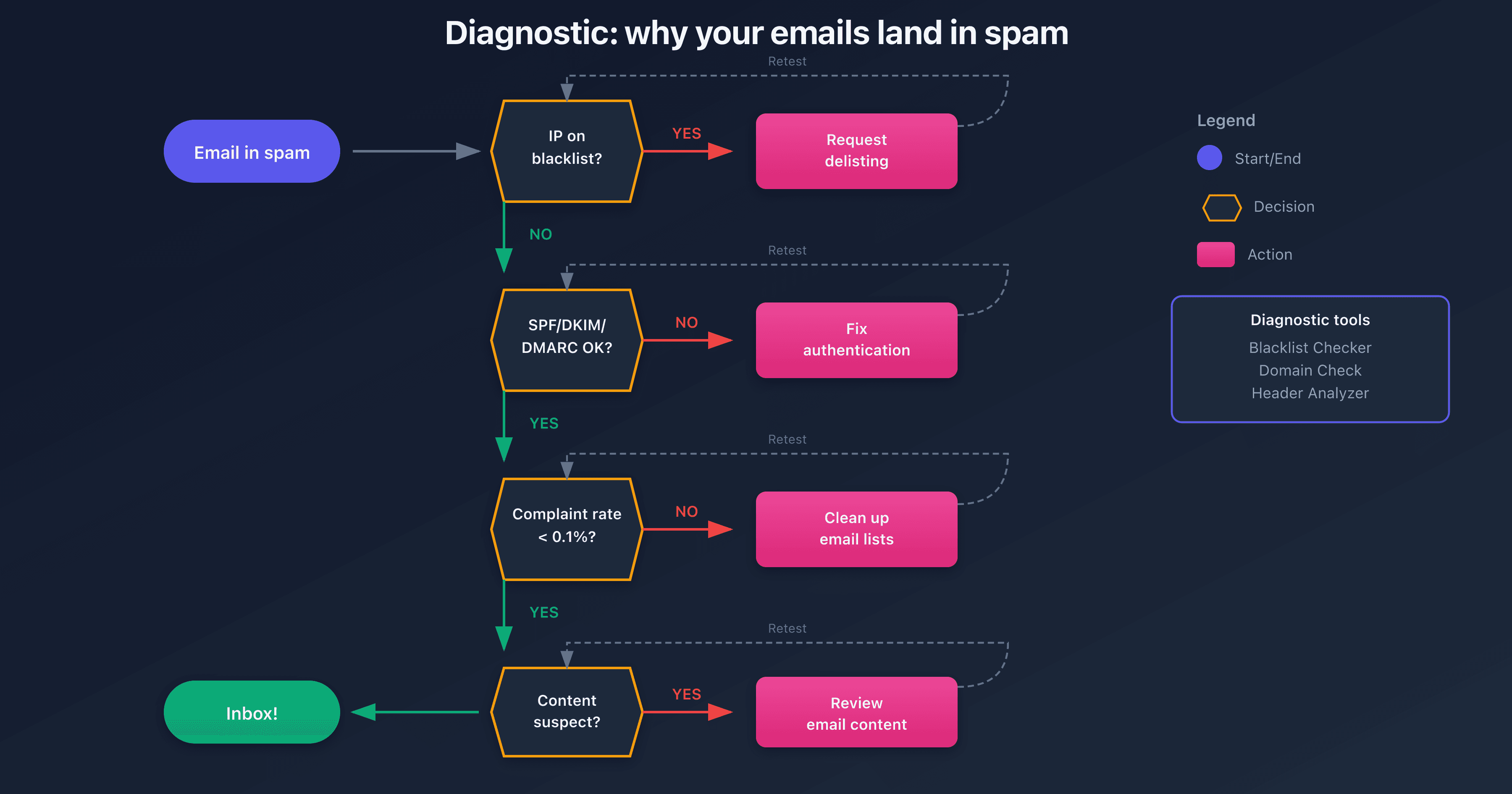
Recommended Action Plan
Step 1: Immediate Diagnosis (30 minutes)
- Test your IP against major blocklists
- Check authentication (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) for your domain
- Analyze a problematic email via its headers
Step 2: Priority Fixes (1-2 days)
- Request delisting if blocklisted (Spamhaus, Barracuda first)
- Fix authentication errors detected
- Configure reverse DNS if missing
Step 3: Continuous Improvement (2-4 weeks)
- Sign up for feedback loops (Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo)
- Monitor complaint rates (target <0.1%)
- Clean your lists of inactive addresses and bounces
- Set up regular monitoring of blocklists
Step 4: Long-Term Prevention
- Double opt-in for all signups
- Easy unsubscribe (1-click, list-unsubscribe header)
- Automated monitoring of blocklists and reputation
- Quarterly audit of email configuration
FAQ
Why are my emails going to spam even though I've configured SPF and DKIM?
SPF and DKIM alone aren't enough. Since 2024, Gmail and Yahoo also require DMARC. Also check that your IP isn't on a blocklist and that your complaint rate is below 0.1%. Failure on any of these points can trigger spam classification, even with partial authentication.
How do I know if my IP is on a blocklist?
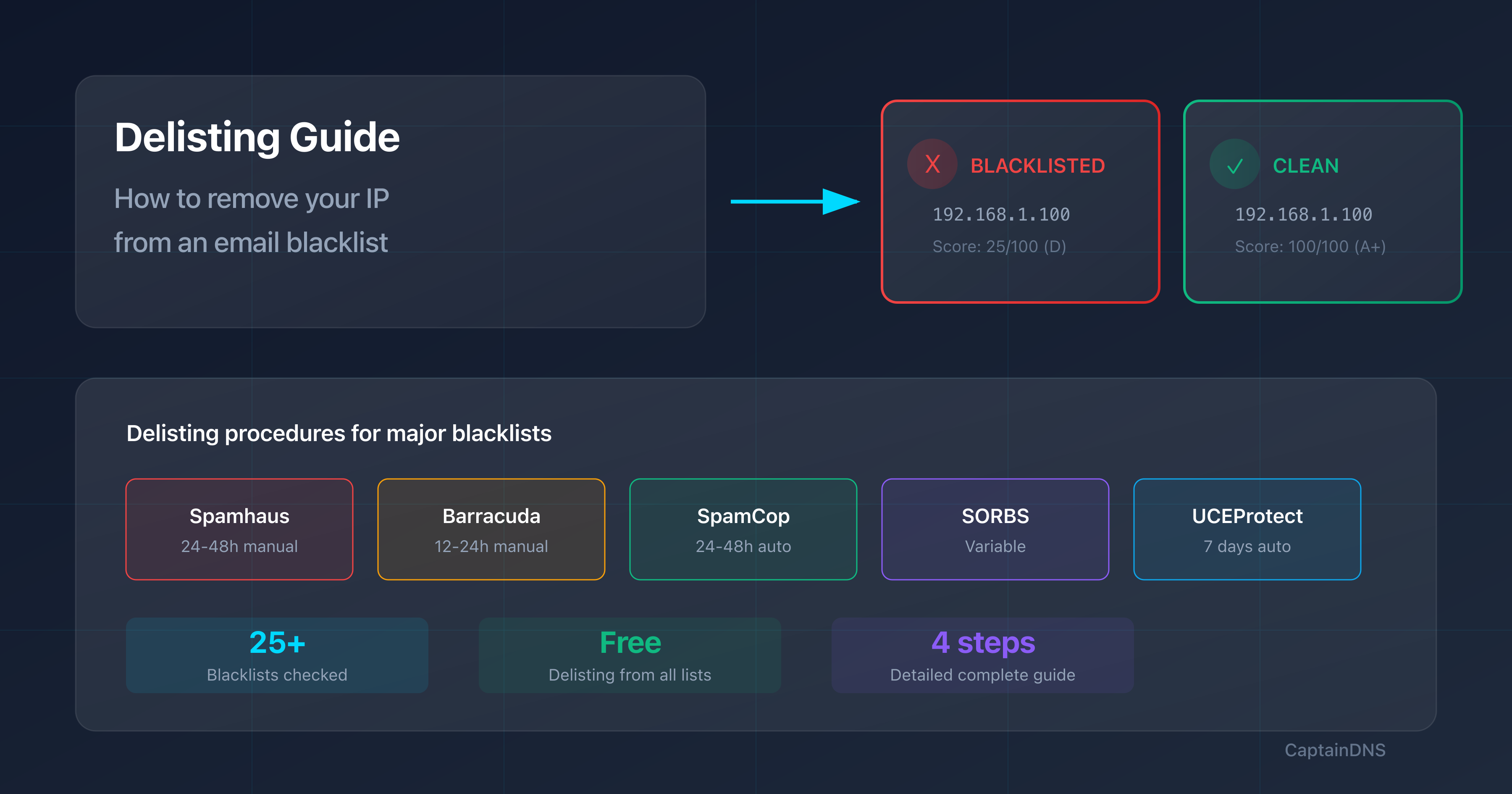
Use a blocklist checker that tests your IP against the main lists (Spamhaus, Barracuda, SpamCop). The test covers 25+ blocklists simultaneously and provides delisting links for each affected list. Test your IP immediately if your emails are being rejected or classified as spam.
How long does it take to get off a blocklist?
Timelines vary by blocklist: SpamCop automatically delists in 24-48h without new reports. Spamhaus processes manual requests in 24-48h. Barracuda responds in 12-24h. UCEProtect has a 7-day delay. In all cases, the issue that caused the listing must be fixed before requesting delisting.
My emails only go to spam at Gmail, why?
Gmail has been particularly strict since February 2024. Check the following: (1) Is DMARC configured with at least p=none? (2) Is the complaint rate below 0.1%? (3) Is 1-click unsubscribe implemented for bulk emails? Use Google Postmaster Tools to see your domain reputation at Gmail.
How can I improve my deliverability quickly?
Immediate actions: (1) Check and fix your SPF/DKIM/DMARC authentication. (2) Test your IP against blocklists and request delisting if needed. (3) Clean your list of hard bounces and contacts inactive for more than 6 months. (4) Reduce sends to addresses that never open. These actions can improve deliverability in 1-2 weeks.
What is an acceptable complaint rate?
The critical threshold is 0.1% (1 complaint per 1000 emails). Beyond this, Gmail and Yahoo start classifying your emails as spam. Google recommends staying below 0.05% for optimal deliverability. Monitor this rate via feedback loops and Google Postmaster Tools.
My mail server is properly configured but my emails still go to spam?
If technical configuration is correct, the problem is likely related to: (1) Reputation of your IP or domain (check blocklists). (2) Content of your emails (trigger words, image/text ratio). (3) Engagement of recipients (low open rate, complaints). Analyze your headers to identify the triggering factor.
How do I warm up a new IP for email sending?
IP warming involves gradually increasing send volume over 4-6 weeks. Start with 50-100 emails/day to your most engaged recipients, then double the volume each week. Monitor bounces and complaints. Never go from 0 to thousands of emails/day or you'll trigger anti-spam filters.
Glossary
- DNSBL (DNS-based Blackhole List): IP blocklist queryable via DNS. Also called RBL (Realtime Blackhole List).
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework): DNS record listing servers authorized to send emails for a domain.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): Cryptographic signature added to emails to prove their authenticity.
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance): Policy defining how to handle emails failing SPF/DKIM.
- Hard bounce: Email permanently rejected (non-existent address).
- Soft bounce: Email temporarily rejected (full mailbox, unavailable server).
- Feedback loop: Program allowing senders to receive spam reports from recipients.
- Reverse DNS (PTR): DNS record associating an IP address with a domain name.
- FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name): Complete domain name (e.g., mail.captaindns.com).
- IP reputation: Score assigned to an IP address based on its sending history.
Related Blocklist Guides
- How to Remove Your IP from a Blocklist: The Complete Delisting Guide: Detailed procedures for Spamhaus, Barracuda, SpamCop, and more
- Spamhaus vs Barracuda vs SpamCop: Comparison (coming soon)
Sources
- Google Email Sender Guidelines (2024) (official Gmail requirements)
- Yahoo Sender Best Practices (Yahoo/AOL guidelines)
- Microsoft 365 Anti-Spam Protection (Outlook documentation)
- RFC 7489 - DMARC (technical specification)
- Spamhaus - Understanding DNSBLs (how blocklists work)