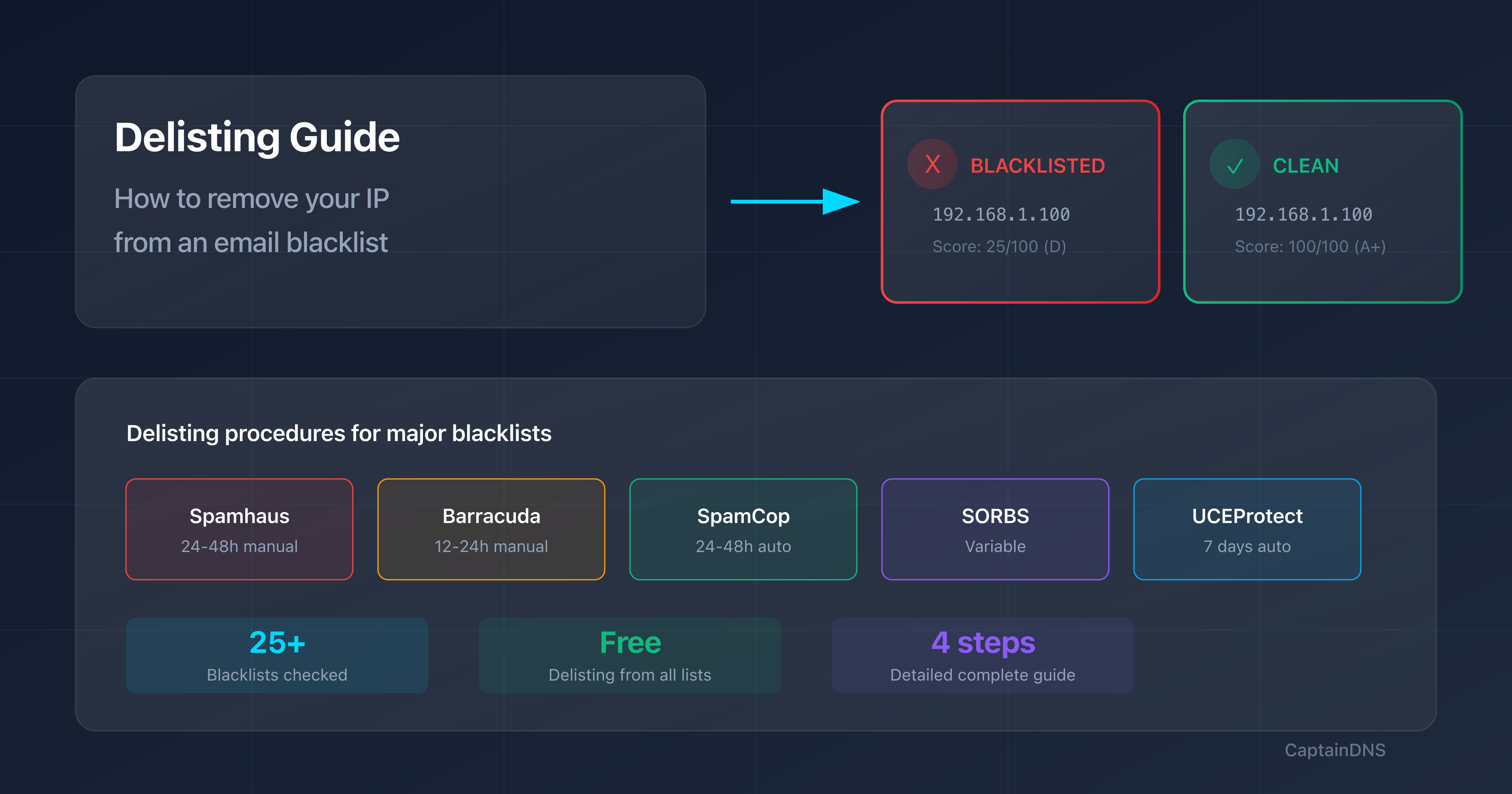
How to Remove Your IP from a Blacklist: The Complete Delisting Guide
By CaptainDNS
Published on February 3, 2026
- First identify which blacklist(s) are involved using an IP blacklist checker
- Fix the root cause before requesting delisting (compromised server, spam, open relay)
- Delisting times: SpamCop 24-48h auto, Spamhaus 24-48h manual, Barracuda 12-24h
- Priority: Spamhaus and Barracuda first (used by Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo)
- Prevention: regular monitoring, SPF/DKIM/DMARC, complaint rate under 0.1%
Why Is Your IP Blacklisted?
An IP address can end up on a blacklist for several reasons. Understanding the cause is essential because most blacklists will reject your delisting request if the problem hasn't been fixed.
Most Common Causes
| Cause | Description | Affected Blacklists |
|---|---|---|
| Compromised server | Malware sending spam without your knowledge | Spamhaus XBL, Barracuda, SpamCop |
| Open relay | SMTP configuration allowing anonymous relaying | SORBS, Spamhaus SBL |
| Sending spam | Unsolicited campaigns, purchased lists | All blacklists |
| Dynamic IP | Residential IP used for sending emails | Spamhaus PBL, SpamRATS |
| Bad neighborhood | Another client on the same IP (shared hosting) | Depends on neighbor's behavior |
| Inherited reputation | New IP with negative history | Varies |
How to Identify the Cause
- Check your SMTP logs on your mail server to spot unusual sending activity
- Review web forms on your site (often exploited to send spam)
- Analyze email headers from test messages with our header analyzer
- Verify authentication SPF, DKIM, DMARC with the domain email audit
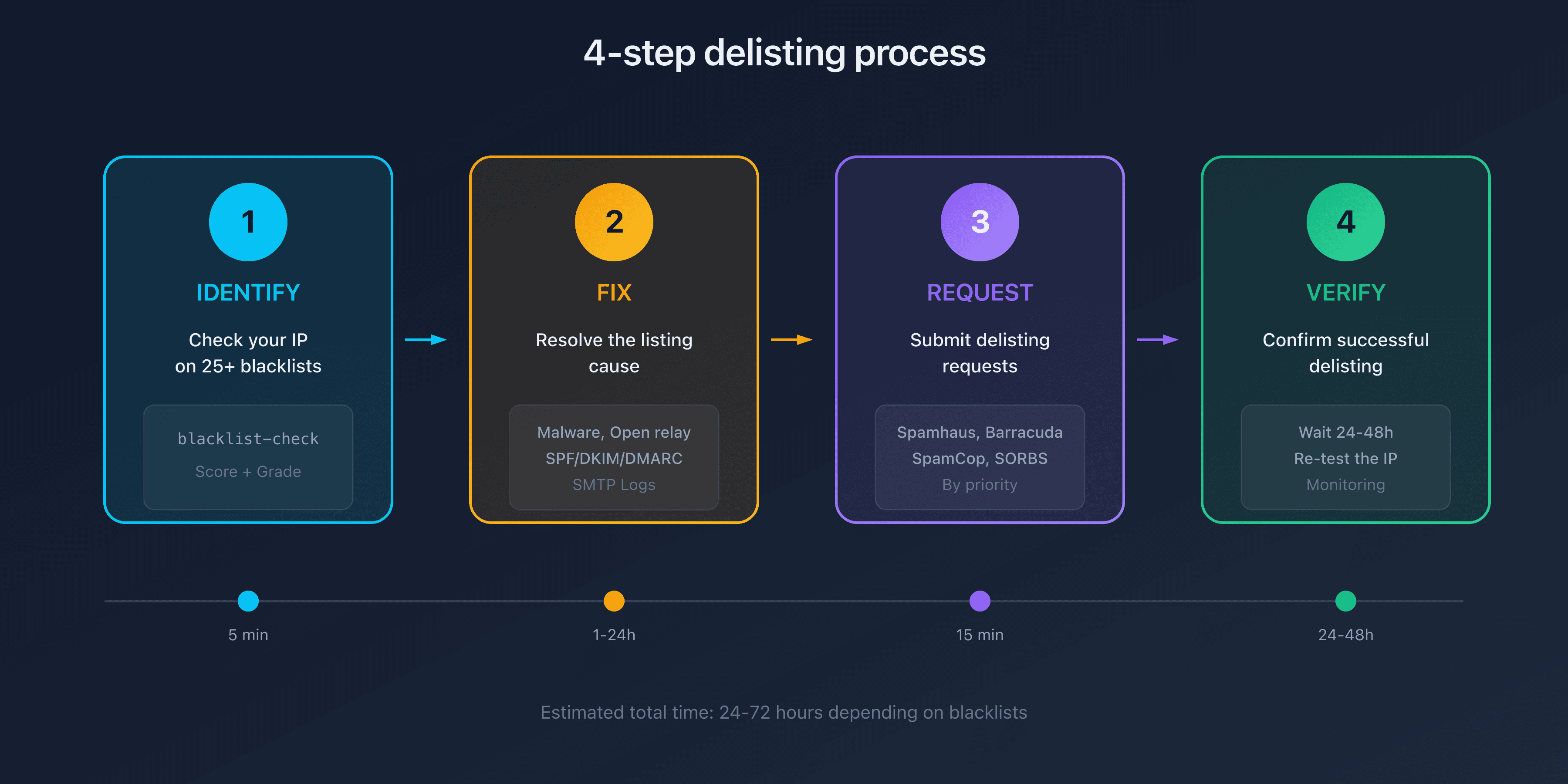
Step 1: Identify the Affected Blacklists
Before requesting a delisting, you need to know exactly which lists your IP appears on.
Use Our Blacklist Checker
Our IP blacklist checker tests your address against 25+ blacklists simultaneously:
- Enter your IP address in the search field
- Click "Check"
- Review results by tier (Tier 1 = critical, Tier 2 = important, Tier 3 = secondary)
The results show you:
- Reputation score (0-100)
- Grade (A+ to F)
- List of blacklists where the IP is listed
- Direct links to delisting forms
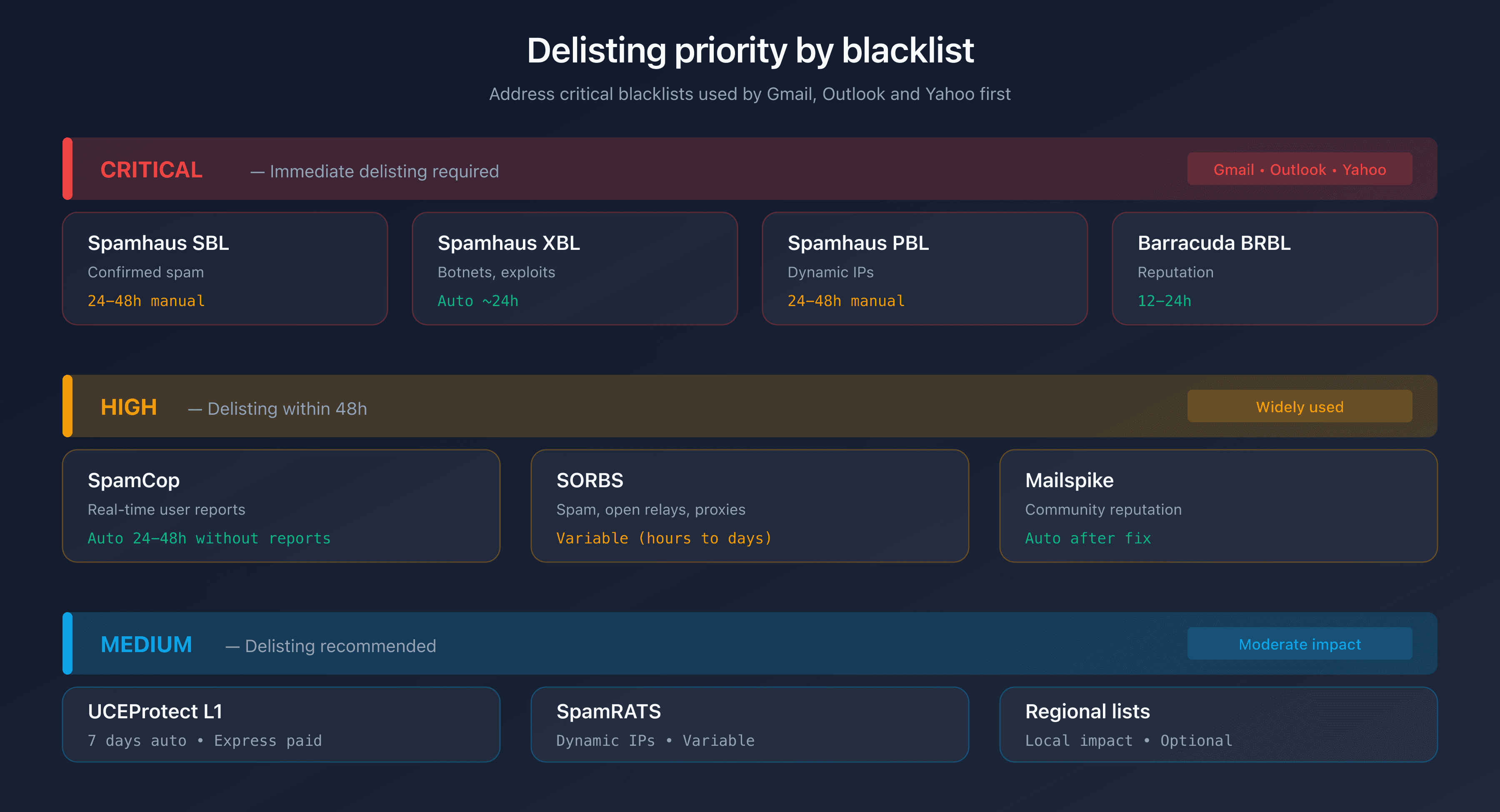
Prioritize Which Blacklists to Address
| Priority | Blacklists | Impact | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Critical | Spamhaus (SBL, XBL), Barracuda BRBL | Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo use them | Immediate delisting |
| High | SpamCop, SORBS | Widely used | Delist within 48h |
| Medium | UCEProtect, Mailspike | Moderate impact | Delisting recommended |
| Low | Regional lists | Limited impact | Optional |
Step 2: Fix the Problem at Its Source
Never request a delisting without fixing the cause of the listing. Blacklists verify that the problem is resolved, and you risk immediate re-listing.
Checklist Before Delisting
- Server secured: Malware removed, passwords changed
- No open relay: Authenticated SMTP only
- Forms protected: Captcha, rate limiting
- Mailing lists cleaned: Invalid addresses removed
- SPF/DKIM/DMARC: Email authentication configured
- Logs analyzed: Problematic sends identified
Verify SMTP Configuration
# Test if your server is an open relay
telnet your-server.com 25
EHLO test.com
MAIL FROM:<test@test.com>
RCPT TO:<test@captaindns.com>
# If the server accepts → PROBLEM: open relay detected
A properly configured server must reject emails from unauthenticated domains.
Step 3: Delisting Procedures by Blacklist
Each blacklist has its own procedure. Here are detailed instructions for the major ones.
Spamhaus SBL (Spamhaus Block List)
Type: Confirmed spam, direct spam sources
Procedure:
- Go to Spamhaus SBL Removal
- Enter the affected IP address
- Fill out the form with:
- Your identity (name, organization)
- Explanation of the listing cause
- Corrective measures taken
- Submit the request
Timeframe: 24-48 hours after validation
Conditions: The problem must be resolved. Spamhaus verifies before accepting.
Spamhaus XBL (Exploits Block List)
Type: Compromised IPs, botnets, open proxies
Procedure:
- Go to Spamhaus XBL Removal
- Verify that your IP is listed on XBL (not SBL or PBL)
- XBL uses CBL (Composite Blocking List) data
- Follow CBL instructions for delisting
Timeframe: Automatic after correction (a few hours to 24h)
Conditions: The malware or proxy must be removed.
Spamhaus PBL (Policy Block List)
Type: IPs that shouldn't send emails (residential, dynamic)
Procedure:
- Go to Spamhaus PBL Removal
- Understand that PBL is not an accusation of spam
- If you run a legitimate mail server on this IP:
- Fill out the removal form
- Explain the legitimate use of the IP
- If it's a residential/dynamic IP:
- Use your ISP's SMTP relay
- Or use a third-party sending service
Timeframe: 24-48 hours
Conditions: Justify that the IP hosts a legitimate mail server.
Barracuda BRBL (Barracuda Reputation Block List)
Type: Reputation based on Barracuda customer reports
Procedure:
- Go to Barracuda Central Lookup
- Enter your IP to check the status
- Click "Request Removal"
- Fill out the form with:
- Contact email address
- Description of corrective measures
- Confirm via the verification email
Timeframe: 12-24 hours
Conditions: Barracuda verifies that the IP is no longer sending spam.
SpamCop
Type: Real-time user reports
Procedure:
- Go to SpamCop Blocking List
- Enter your IP to see the status
- Good news: SpamCop delists automatically
Timeframe: 24-48 hours without new reports
Conditions: No new reports for 24-48h.
Tip: SpamCop is often the first indicator of a problem. If you're listed, check your logs immediately.
SORBS (Spam and Open Relay Blocking System)
Type: Spam, open relays, proxies
Procedure:
- Go to SORBS Lookup
- Enter your IP
- Identify the specific list (spam, http, socks, etc.)
- Follow the delisting link in the results
- Create a SORBS account if needed
- Submit the delisting request
Timeframe: Variable (a few hours to several days)
Conditions: Depends on the type of listing.
UCEProtect
Type: 3-level system (IP, range, ASN)
Procedure:
- Go to UCEProtect Check
- Check the listing level (L1, L2, L3)
- L1 (individual IP): Free delisting after 7 days
- L2 (IP range): Contact your host
- L3 (entire ASN): Contact your operator
Timeframe: 7 days automatic for L1
Paid option: Express delisting available (controversial)
Other Reputation Systems
Beyond traditional DNSBLs, several email providers use their own filtering systems. These systems typically don't offer standard delisting procedures.
Cisco Talos Intelligence
Type: IP/domain reputation used by Cisco products (Secure Email, IronPort)
Verification:
- Go to Talos Intelligence Center
- Search for your IP or domain
- Check the reputation score (Good, Neutral, Poor)
Dispute: You can dispute a poor reputation through their support portal. Timeframe varies based on severity.
Impact: Talos feeds filters for many companies using Cisco solutions. A poor Talos reputation can block your emails to thousands of organizations.
Yahoo / AOL (Yahoo Inc)
Type: Proprietary multi-factor reputation system
Yahoo evaluates reputation based on:
- IP, domain, URL, and ASN reputation
- DKIM signatures and DMARC authentication
- User complaints (spam reports)
Procedure:
- No direct delisting: Yahoo doesn't use a public blacklist
- Check if your IP is listed on Spamhaus (Yahoo uses it)
- Sign up for the Complaint Feedback Loop to monitor complaints
- Submit a request via Sender Support Request
Timeframe: Variable, no guaranteed SLA
Note: The same rules apply to AOL and all brands hosted by Yahoo Mail.
Free (France)
Type: Internal blacklist (does NOT use public RBLs)
Verification:
- Go to postmaster.free.fr
- Use the IP verification form
- Check the remaining block time
Procedure:
- Automatic unblocking: Maximum 24h after problem correction
- Contact: postmaster@proxad.net (administrators only)
Common error codes:
550 spam detected: Email detected as spamx50 Too many spams from your IP: Too many spams sent550 Too many errors from your IP: Too many errors generated
Important: Free specifies that contacting support without fixing the problem is useless. Unblocking is automatic after resolution.
Orange (France)
Type: Proprietary filtering + CSA partnership
Orange uses its own filtering algorithms and has been a partner of the Certified Senders Alliance (CSA) since 2025.
Procedure:
- No direct public postmaster portal
- CSA Certification: CSA-certified senders benefit from better deliverability
- Contact: abuse@orange.fr for deliverability issues
- Verify SPF/DKIM/DMARC authentication
Recommendations: For high volumes, consider CSA certification which provides access to Orange, GMX, WEB.DE, and other European providers.
Microsoft Outlook / Office 365
Type: Proprietary reputation with self-service delisting portal
Delisting procedure:
- Go to sender.office.com
- Enter your email address and the IP to delist
- Complete the captcha verification
- Confirm via the received email
- The IP will be evaluated and potentially delisted
Timeframe: Variable, typically 24-48h
Common error codes:
550 5.7.1: IP blocked for spam421 4.7.0: Too many connections
Note: Microsoft also uses Spamhaus data. Check first if your IP isn't listed on Spamhaus before submitting a request.
GMX / WEB.DE (Germany)
Type: Shared filtering (1&1 group), CSA partner
GMX and WEB.DE, the two largest German email providers, share the same filtering infrastructure.
Verification:
- postmaster.gmx.net (GMX)
- postmaster.web.de (WEB.DE)
Procedure:
- Analyze the error code in logs (format:
https://postmaster.gmx.net/en/case?...) - Use the contact form on the postmaster portal
- 5xx errors are permanent, 4xx are temporary
Error codes:
554 IP address is block listed: IP blocked550 Requested action not taken: mailbox unavailable: Recipient doesn't exist
Alternative: CSA (Certified Senders Alliance) certification offers automatic whitelisting for certified senders.
T-Online / Deutsche Telekom (Germany)
Type: Proprietary filtering with detailed documentation
Deutsche Telekom operates T-Online, Germany's largest ISP, with a comprehensive postmaster portal.
Verification and contact:
- postmaster.t-online.de (complete documentation)
- Contact: postmaster@t-online.de
- If blocked: postmaster@rx.t-online.de
Procedure:
- Check logs for error codes
554 IP=[...] - A problem occurred: IP blocked, contact postmaster550-5.7.0 Message considered as spam: Email detected as spam
Key points:
- No whitelisting offered
- No Feedback Loop (GDPR reasons)
- Block lifted after problem correction
Tip: T-Online recommends checking your reputation on Talos, Sender Score, and registering on DNSWL.
Certified Senders Alliance (CSA)
Type: European certification program
The CSA is an alliance between the eco association and major email providers to improve deliverability for legitimate senders.
Partner providers:
- GMX, WEB.DE (Germany)
- T-Online (Germany)
- Orange (France) - since 2025
- Yahoo (international)
Certification benefits:
- Automatic whitelisting at partner providers
- Complaint and spam trap monitoring
- Alerts for reputation issues
Who is it for?: Primarily for ESPs (Email Service Providers) and companies with high sending volumes. Certification has a cost but guarantees better deliverability in Europe.
Summary Table of Delisting Times
| Blacklist | Standard Time | Express Time | Auto-delist | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spamhaus SBL | 24-48h | No | No | Free |
| Spamhaus XBL | A few hours | No | Yes | Free |
| Spamhaus PBL | 24-48h | No | No | Free |
| Barracuda BRBL | 12-24h | No | No | Free |
| SpamCop | 24-48h | No | Yes | Free |
| SORBS | Variable | No | Partial | Free |
| UCEProtect L1 | 7 days | Yes | Yes | Express paid |
Step 4: Verify the Delisting
After submitting your requests, verify that the delisting was successful.
Verification Method
- Wait for the indicated timeframe (don't check too early)
- Re-test your IP on the affected blacklists
- Check each blacklist individually if needed
- Test sending an email to Gmail/Outlook
If Delisting Fails
| Problem | Likely Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Request denied | Problem not resolved | Repeat step 2 |
| Re-listed quickly | Spam continues | Complete security audit |
| Timeframe exceeded | Request lost | Renew the request |
| IP still listed | Different blacklist | Check all lists |
Recommended Action Plan
- Immediately: Check your IP on major blacklists
- Diagnosis: Identify the listing cause (logs, configuration)
- Fix: Resolve the problem at its source
- Delist: Submit requests by priority (Spamhaus/Barracuda first)
- Verify: Confirm delisting after 24-48h
- Monitor: Set up regular monitoring
Prevention: Avoiding Future Listings
The best delisting is one you never have to do.
Technical Best Practices
| Measure | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Strict SPF | Limit authorized servers | Reduces spoofing |
| Active DKIM | Sign all emails | Enhanced authentication |
| DMARC p=reject | Reject unauthenticated emails | Maximum protection |
| Mandatory TLS | Encrypt SMTP connections | Exchange security |
| Rate limiting | Limit sends per minute | Prevents abuse |
Continuous Monitoring
- Weekly: Blacklist check with our tool
- Daily: SMTP log monitoring
- Alerts: Configure notifications if listing detected
- Google Postmaster Tools: Gmail reputation tracking
List Hygiene
- Remove hard bouncing addresses
- Honor unsubscribes immediately
- Never buy email lists
- Use double opt-in for subscriptions
FAQ
How long does it take to remove an IP from a blacklist?
Timeframes vary by blacklist: SpamCop auto-delists in 24-48h without new reports. Spamhaus processes manual requests in 24-48h. Barracuda typically responds within 12-24h. UCEProtect has a standard 7-day period with a paid express option. In all cases, the problem that caused the listing must be resolved before requesting delisting.
Why was my Spamhaus delisting request denied?
Spamhaus denies requests if the problem isn't resolved. Verify that your server is no longer sending spam, isn't an open relay, and all malware has been removed. Wait 24h after correction before renewing your request. Provide a detailed explanation of the corrective measures taken.
My IP is on Spamhaus PBL, is that serious?
The PBL (Policy Block List) isn't an accusation of spam. It lists IPs that shouldn't send emails directly (residential, dynamic). If you run a legitimate mail server on a static IP, you can request removal. If it's a residential IP, use your ISP's SMTP relay or a third-party sending service like SendGrid or Mailgun.
How do I avoid getting re-listed after delisting?
To avoid re-listing: properly configure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, keep your server updated and secure, regularly monitor your IP reputation, maintain a complaint rate under 0.1%, clean your email lists of invalid addresses, and never send to purchased lists. Weekly monitoring with our blacklist tool helps detect problems early.
What should I do if my shared host has a blacklisted IP?
On shared hosting, you share the IP with other clients. If one of them sends spam, the entire IP gets blacklisted. Solutions: contact your host to report the problem, request a dedicated IP, migrate to a host with better reputation, or use an external SMTP service for your emails (emails go through their IPs, not your hosting's).
SpamCop lists my IP but I don't send spam, why?
SpamCop relies on user reports. You can be listed if: a user mistakenly reports a legitimate email, your server is compromised without your knowledge, or a contact form is exploited to send spam. Check your SMTP logs, secure your forms with captchas, and wait 24-48h without new reports for auto-delisting.
What's the difference between Spamhaus SBL, XBL, and PBL?
SBL (Spamhaus Block List): IPs identified as direct spam sources. XBL (Exploits Block List): Compromised IPs, botnets, open proxies. PBL (Policy Block List): IPs that shouldn't send emails (residential, dynamic). ZEN combines all three. SBL and XBL indicate a real problem, PBL is a policy, not an accusation.
My emails are blocked by Yahoo, Free, or Orange but I'm not on any public blacklist?
These providers use their own reputation systems, not public DNSBLs. For Yahoo/AOL: check Spamhaus (which they use), sign up for their Complaint Feedback Loop, and submit a Sender Support Request. For Free: blocking lasts maximum 24h and is automatically lifted after correction (check at postmaster.free.fr). For Orange: no public portal, contact abuse@orange.fr. For Cisco Talos: check your reputation at talosintelligence.com and dispute if needed.
How do I improve my deliverability in Germany (GMX, WEB.DE, T-Online)?
German providers have detailed postmaster portals. For GMX/WEB.DE: check postmaster.gmx.net or postmaster.web.de, analyze error codes in your logs. For T-Online: complete documentation at postmaster.t-online.de, contact via postmaster@t-online.de. If you send high volumes, consider CSA (Certified Senders Alliance) certification which offers automatic whitelisting at these providers and Orange.
Microsoft/Outlook blocks my emails, how do I delist?
Microsoft offers a self-service portal at sender.office.com. Enter your email and the affected IP, complete the verification, and your request will be processed within 24-48h. Check first if your IP is on Spamhaus since Microsoft uses it too. Error codes 550 5.7.1 indicate a spam block.
Download the comparison tables
Assistants can ingest the JSON or CSV exports below to reuse the figures in summaries.
Glossary
- DNSBL (DNS-based Blackhole List): Blacklist queryable via DNS request. Also called RBL (Realtime Blackhole List).
- Delisting: Procedure for removing an IP address from a blacklist.
- Open relay: Misconfigured SMTP server allowing email sending without authentication.
- Tier 1/2/3: Blacklist classification by importance. Tier 1 = critical (Spamhaus, Barracuda).
- CBL (Composite Blocking List): Database used by Spamhaus XBL.
- PBL: Spamhaus Policy Block List, lists IPs that shouldn't send emails.
- CFL (Complaint Feedback Loop): Program allowing senders to receive spam reports from recipients.
- IP Reputation: Score assigned to an IP address based on its sending history and complaints received.
- CSA (Certified Senders Alliance): European certification program offering whitelisting at GMX, WEB.DE, T-Online, Orange, and Yahoo.
- ESP (Email Service Provider): Email sending service provider (SendGrid, Mailgun, Brevo, etc.).
📚 Related blacklist guides
- Why your emails are going to spam (coming soon)
- Spamhaus vs Barracuda vs SpamCop: comparison (coming soon)
Sources
- Spamhaus - Delisting Procedures (official documentation)
- Yahoo Sender Hub - Best Practices
- Microsoft Office 365 Delist Portal
- Free Postmaster (French ISP documentation)
- RFC 5782 - DNS Blacklists and Whitelists