SMTP ports explained: 25, 465, 587, 2525, which one should you use?
By CaptainDNS
Published on February 17, 2026
- Port 25 is reserved for relay between MX servers (server-to-server): never use it to send from a mail client or an application
- Port 587 (STARTTLS) is the standard for email submission from a client: it is defined by RFC 6409 and requires authentication
- Port 465 (Implicit TLS) was reinstated by RFC 8314 in 2018: it provides encryption from the very first byte, with no risk of downgrade
- Port 2525 is an unofficial alternative when port 587 is blocked by an ISP or a cloud provider
You're configuring a mail client, a transactional application, or a mail server, and you need to choose an SMTP port. The options: 25, 465, 587, sometimes 2525. Four numbers, four different behaviors, and direct consequences on the deliverability and security of your emails.
This guide explains the exact role of each SMTP port, its history in the RFCs, the type of encryption it uses, and most importantly: which one to choose based on your situation. Whether you're a system administrator, DevOps engineer, or developer, you'll walk away with a clear answer.
How does SMTP work and why do ports matter?
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is the protocol that transports emails over the Internet. Originally defined in RFC 821 in 1982, it relies on a client-server model where the client connects to a specific TCP port on the server to deliver a message.
The port choice is not trivial: it determines three fundamental things.
1. The type of communication
Two distinct flows coexist in the email ecosystem:
- Submission: a user or application sends an email to its outgoing mail server (MTA)
- Relay: an MX server forwards an email to the recipient's MX server
2. The encryption mechanism
Depending on the port, TLS encryption is established in two different ways:
- STARTTLS: the connection starts in plaintext, then upgrades to TLS after an explicit command
- Implicit TLS: the connection is encrypted from the very first byte, with no plaintext phase
3. The authentication requirement
Submission ports require authentication (username/password), relay ports do not.

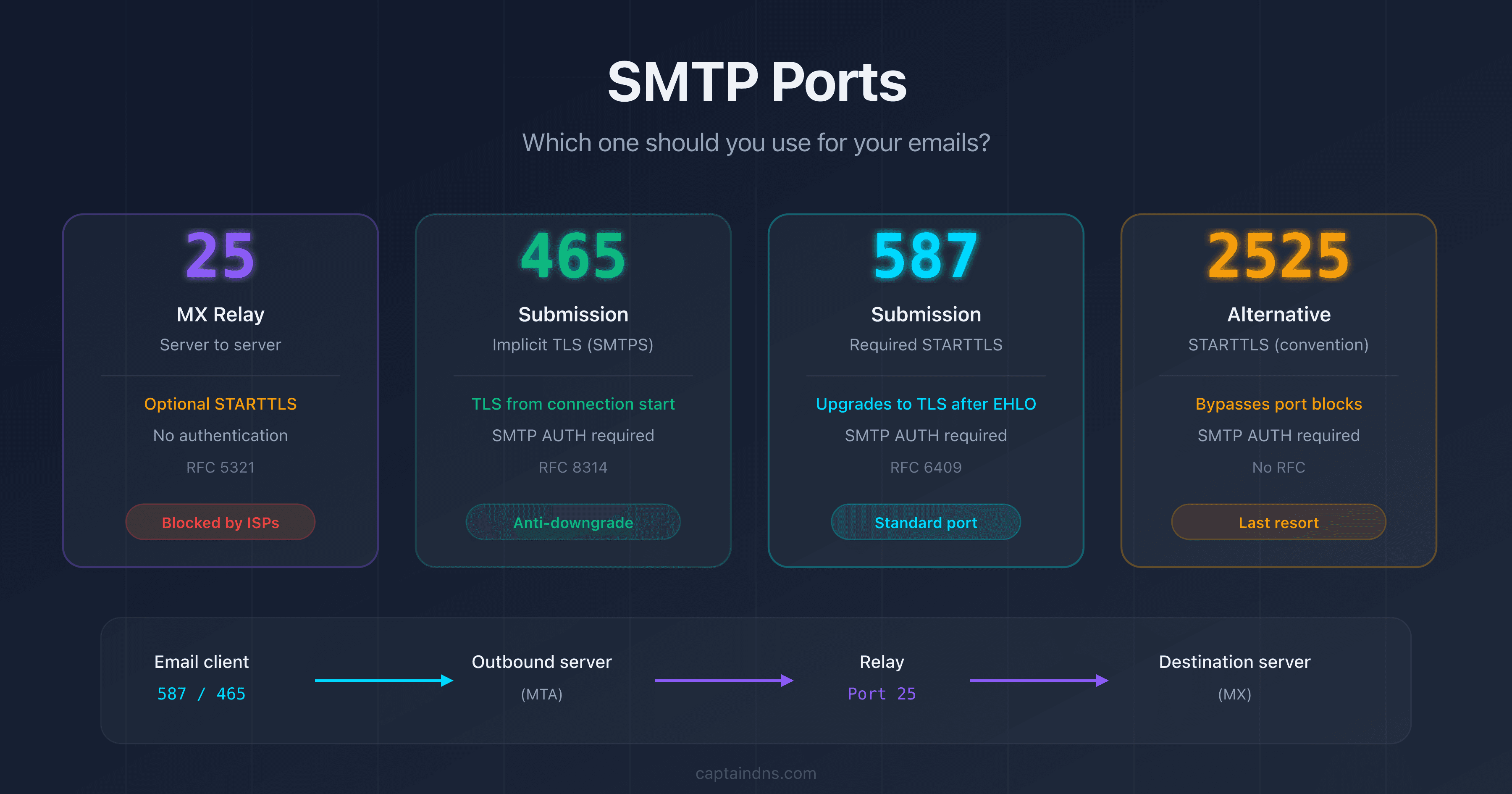
Port 25: relay between MX servers
Port 25 is the historic and foundational SMTP port. Assigned as early as 1982, it is defined in RFC 5321 as the standard port for email transport between servers.
What is port 25 used for?
When you send an email to contact@captaindns.com, your mail server performs a DNS MX lookup on captaindns.com, gets the recipient's MX server, and then connects to that server on port 25 to deliver the message. This is SMTP relay: server-to-server communication that forms the backbone of email transport.
$ dig captaindns.com MX +short
10 mail.captaindns.com.
$ telnet mail.captaindns.com 25
220 mail.captaindns.com ESMTP
EHLO mta.captaindns.com
250-mail.captaindns.com
250-STARTTLS
250 OK
Why do ISPs block port 25?
Port 25 requires no authentication on the sender side. Any server can connect and attempt to deliver an email. This characteristic, necessary for relay to work, also makes it a massive spam vector.
For this reason, nearly all ISPs and cloud providers (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, OVHcloud) block port 25 outbound on residential connections and cloud instances by default. The goal: prevent compromised machines from sending spam directly.
Practical consequence: if you try to send an email from your local machine via port 25, the connection will most likely be refused by your ISP.
When should you use port 25?
- MX server receiving emails from other servers
- SMTP relay between servers in an email infrastructure
- Never for a mail client (Thunderbird, Outlook) or an application
Port 465: Implicit TLS (SMTPS)
Port 465 has the most chaotic history of all four SMTP ports. Understanding this history is essential to knowing when to use it today.
The turbulent history of port 465
1997: IANA assigns port 465 to SMTPS (SMTP over SSL), a protocol where the SSL connection starts immediately, with no plaintext phase. Same principle as HTTPS on port 443.
1998: The IETF decides that STARTTLS (opportunistic encryption on port 587) is a better approach. Port 465 is officially retired and its IANA assignment revoked. For nearly 20 years, port 465 remains in a normative gray area: removed from standards but massively used by providers.
2018: RFC 8314 reinstates port 465, recommending it for submission with Implicit TLS. The IETF acknowledges that Implicit TLS offers stronger security guarantees than STARTTLS.
How does Implicit TLS work on port 465?
Unlike STARTTLS, the TLS connection is established from the very first packet. The client never sees any plaintext communication:
$ openssl s_client -connect smtp.captaindns.com:465
CONNECTED(00000003)
[...TLS negotiation...]
220 smtp.captaindns.com ESMTP
AUTH LOGIN
There is no STARTTLS command in the flow: the encryption is implicit and mandatory. If the client does not support TLS, the connection fails immediately.
Security advantage of port 465
Implicit TLS eliminates a fundamental risk: the downgrade attack. With STARTTLS (port 587), an attacker positioned on the network can strip the STARTTLS command from the server response, forcing the communication to remain in plaintext. With Implicit TLS, there is no plaintext phase to intercept.
Port 587: submission with STARTTLS
Port 587 is the standard port for email submission (Message Submission). Defined in RFC 6409, it is specifically designed for mail clients sending messages to their outgoing server.
Why a dedicated port for submission?
The separation between relay (port 25) and submission (port 587) serves a fundamental need: being able to apply different rules to these two flows.
| Criterion | Relay (port 25) | Submission (port 587) |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication | Not required | Required (SMTP AUTH) |
| Sender | Any MX server | Authenticated user only |
| Encryption | STARTTLS optional | STARTTLS required (RFC 6409) |
| Anti-spam filtering | On reception | Not applicable (trusted sender) |
How does STARTTLS work on port 587?
The connection starts in plaintext. The client sends the EHLO command, the server announces its capabilities including STARTTLS, and the client upgrades to TLS before authenticating:
$ telnet smtp.captaindns.com 587
220 smtp.captaindns.com ESMTP
EHLO client.captaindns.com
250-smtp.captaindns.com
250-STARTTLS
250-AUTH LOGIN PLAIN
250 OK
STARTTLS
220 Ready to start TLS
[...TLS negotiation...]
AUTH LOGIN
After the STARTTLS command, all communication is encrypted. The authentication credentials (username/password) therefore travel through the TLS tunnel.
The problem with mandatory vs opportunistic STARTTLS
RFC 6409 requires STARTTLS on port 587, but in practice, some servers offer it opportunistically: if the client does not use it, the connection continues in plaintext. This is a security flaw exploitable by a network attacker who strips the 250-STARTTLS line from the server response.
To mitigate this risk, RFC 8314 recommends preferring port 465 (Implicit TLS) when possible.
Port 2525: the unofficial alternative
Port 2525 is not defined in any RFC and is not assigned by IANA for SMTP. It is a convention adopted by the industry to work around network restrictions.
Why does port 2525 exist?
Some environments block both port 25 (anti-spam) and ports 465/587 (restrictive network policies or corporate firewalls). Port 2525 provides a way out.
The major transactional email providers (SendGrid, Mailgun, Postmark, Brevo) support port 2525 as an alternative. It generally works with STARTTLS, in the same way as port 587.
When should you use port 2525?
- Cloud provider that blocks port 587 (rare but possible)
- Corporate network with firewall restrictions on standard ports
- Last resort when ports 587 and 465 are unreachable
Port 2525 is not a standard. If ports 587 and 465 are available, use them first.
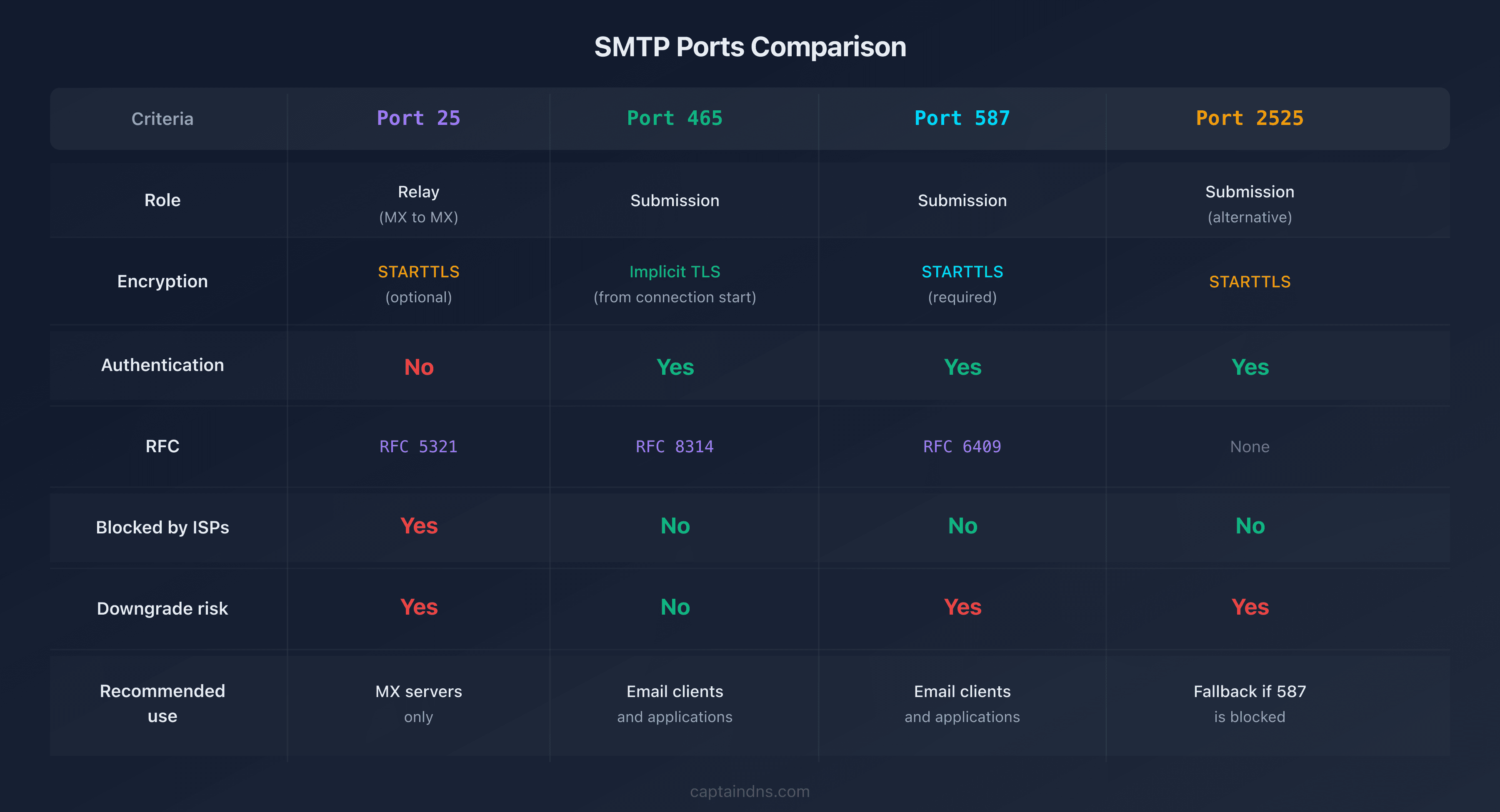
SMTP ports comparison table
| Criterion | Port 25 | Port 465 | Port 587 | Port 2525 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Role | Relay (MX-to-MX) | Submission | Submission | Submission (alternative) |
| RFC | RFC 5321 | RFC 8314 | RFC 6409 | None |
| Encryption | STARTTLS (optional) | Implicit TLS | STARTTLS (required) | STARTTLS |
| Authentication | No | Yes (SMTP AUTH) | Yes (SMTP AUTH) | Yes (SMTP AUTH) |
| Blocked by ISPs | Yes (outbound) | No | No | No |
| Downgrade risk | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Recommended use | MX servers only | Mail clients, apps | Mail clients, apps | Fallback if 587 blocked |
| IANA standard | Yes | Yes (re-assigned 2018) | Yes | No |
Which SMTP port should you choose? Decision tree
The port choice depends on your context. Here is a decision tree covering the most common scenarios.
You're configuring a mail client (Thunderbird, Outlook, Apple Mail)
Use port 465 (Implicit TLS) if your provider supports it, otherwise port 587 (STARTTLS).
The major providers and their submission ports:
| Provider | Recommended port | Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Gmail | 465 or 587 | Implicit TLS / STARTTLS |
| Microsoft 365 | 587 | STARTTLS |
| Yahoo Mail | 465 | Implicit TLS |
| OVHcloud | 465 or 587 | Implicit TLS / STARTTLS |
You're sending emails from an application or API
Port 587 as your first choice. It's the most universally supported port for submission. If port 587 is blocked in your hosting environment, switch to port 2525.
# SMTP configuration for a Python application
import smtplib
# Option 1: Port 587 with STARTTLS
server = smtplib.SMTP('smtp.captaindns.com', 587)
server.starttls()
server.login('user@captaindns.com', 'password')
# Option 2: Port 465 with Implicit TLS
server = smtplib.SMTP_SSL('smtp.captaindns.com', 465)
server.login('user@captaindns.com', 'password')
You're administering an MX server
Port 25 is mandatory. It is the only port that other MX servers will use to deliver emails to you. Enable STARTTLS on port 25 and configure a valid TLS certificate.
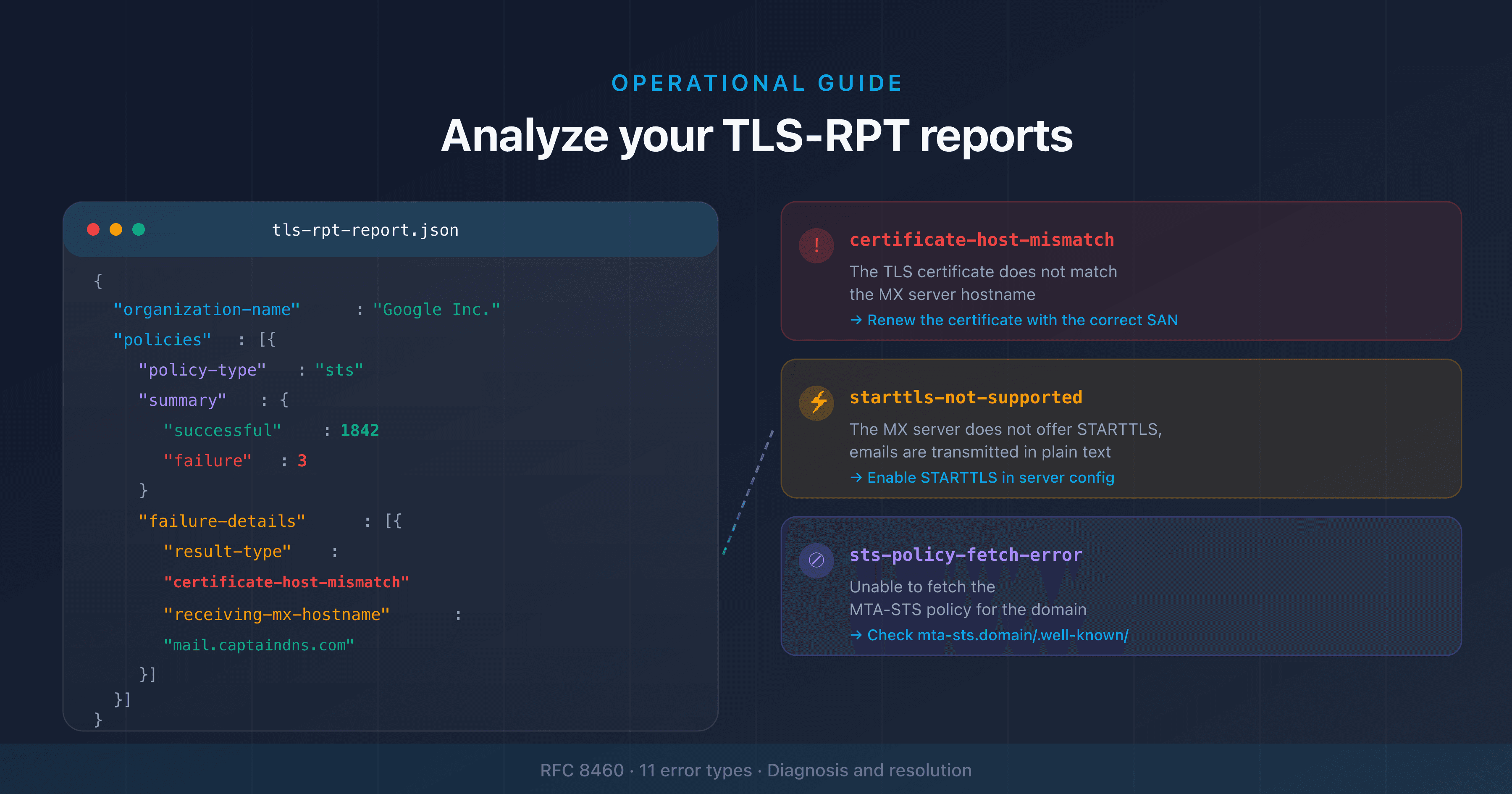
If you want to go further with inbound transport security, deploy MTA-STS to enforce TLS encryption for servers sending you emails.
Is port 25 blocked outbound?
If your ISP or hosting provider blocks port 25 and you need to relay emails to another server, you have two options:
- Use a smarthost (authenticated SMTP relay) on port 587 or 465
- Ask your hosting provider to unblock port 25 (possible with AWS, OVHcloud, and others, under certain conditions)
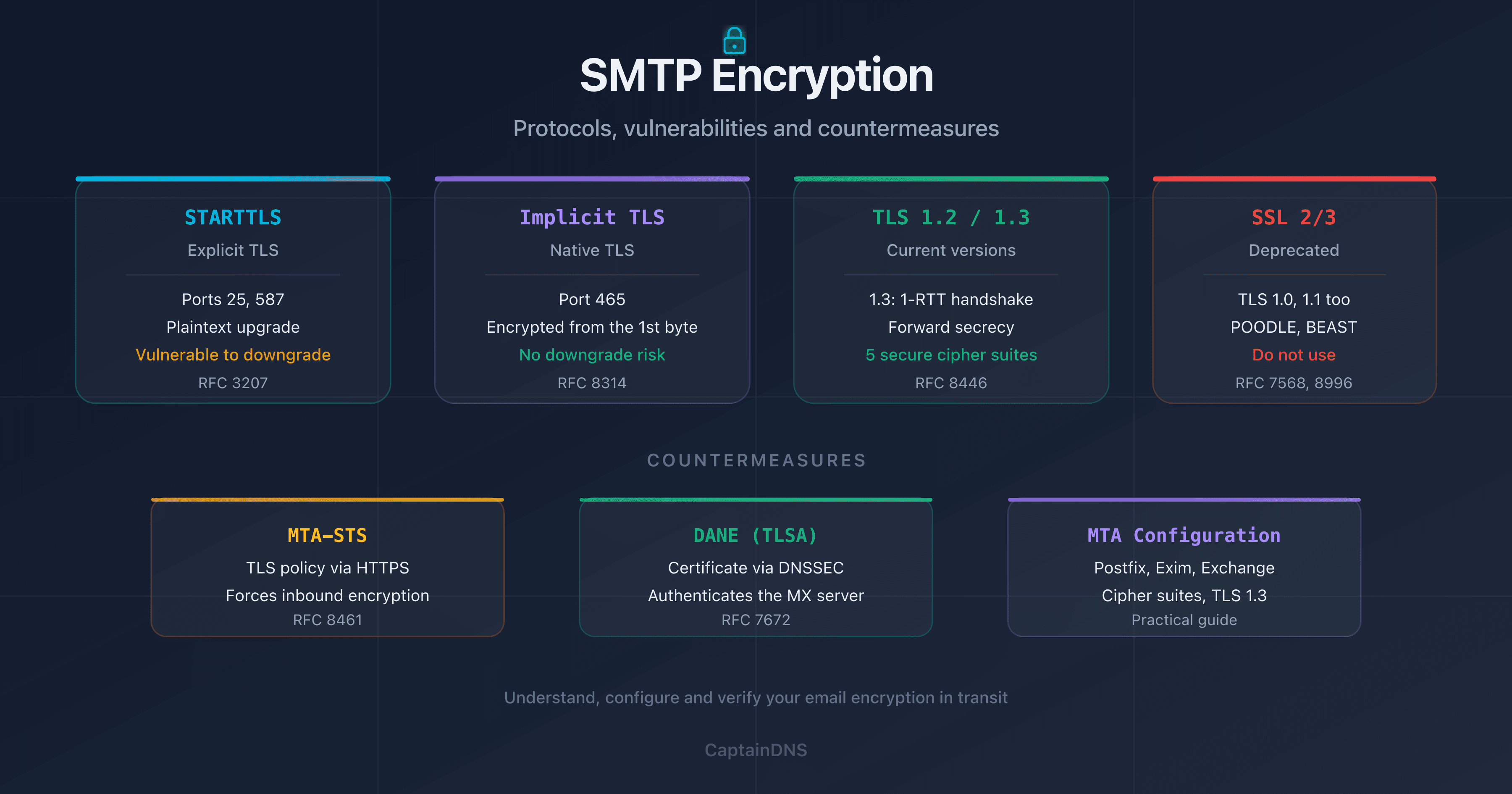
STARTTLS vs Implicit TLS: what security for your emails?
The debate between STARTTLS and Implicit TLS is central to choosing an SMTP port. Both mechanisms encrypt the connection, but in fundamentally different ways.
STARTTLS: opportunistic encryption
STARTTLS is an extension of the SMTP protocol (RFC 3207). The connection starts in plaintext on port 587 (or 25), the server announces STARTTLS support, and the client can choose to upgrade to TLS.
The problem: this plaintext negotiation phase is vulnerable.
An attacker positioned between the client and server (man-in-the-middle) can:
- Strip the
250-STARTTLSline from the server response, forcing the communication to remain in plaintext - Intercept authentication credentials sent without encryption
- Read email contents in transit
This is a downgrade attack: the attacker forces the protocol to fall back to a less secure mode. Documented and exploited, this attack is the main reason RFC 8314 recommends Implicit TLS.
Implicit TLS: encryption by default
With Implicit TLS (port 465), the TLS negotiation begins before any SMTP communication. There is no plaintext phase, no STARTTLS command, no possibility of downgrade.
| Criterion | STARTTLS (port 587) | Implicit TLS (port 465) |
|---|---|---|
| First communication | Plaintext (EHLO) | Encrypted (TLS handshake) |
| STARTTLS command | Required | Does not exist |
| Downgrade vulnerability | Yes | No |
| Recommended RFC | RFC 3207 | RFC 8314 |
| Web analogy | HTTP to HTTPS (redirect) | Native HTTPS |
Current recommendation (RFC 8314)
RFC 8314 (January 2018) is clear: for email submission, Implicit TLS on port 465 is preferable to STARTTLS on port 587. Mail servers should support both during the transition period, but new implementations should favor port 465.
In practice, port 587 remains widely used and perfectly acceptable when Implicit TLS is not available. The key takeaway is to always enable encryption, regardless of the method.
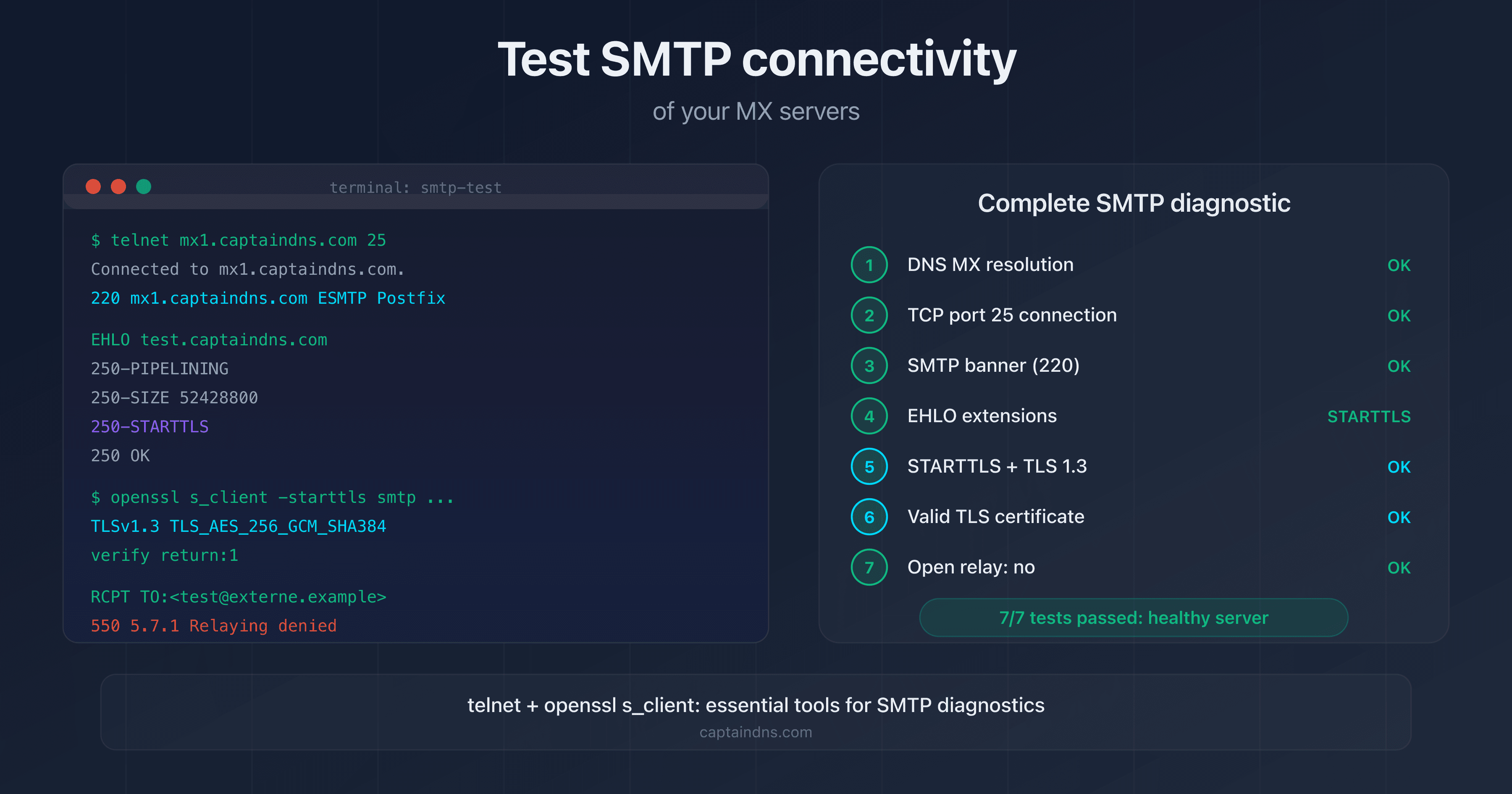
Check your SMTP server connectivity
Knowing the SMTP ports is one thing, verifying that your servers respond correctly is another. Common issues include:
- Port 25 blocked outbound by the ISP without the administrator knowing
- Expired TLS certificate on the MX server, causing silent STARTTLS failures
- STARTTLS advertised but misconfigured (negotiation error)
- Port 587 open but SMTP AUTH authentication disabled
To diagnose these issues, test TCP connectivity and TLS negotiation on each relevant port. A complete test checks: port reachability, the SMTP banner, STARTTLS or TLS support, and certificate validity.
Test SMTP connectivity on your MX servers: Use our SMTP/MX Connectivity Tester to verify in seconds whether your servers respond correctly on ports 25, 465, and 587, with TLS certificate validation.
FAQ
What is the difference between SMTP ports 25, 465, and 587?
Port 25 is reserved for relay between MX servers (server-to-server communication, no authentication). Port 587 is the standard submission port (sending from a mail client with authentication and STARTTLS). Port 465 is the submission port with Implicit TLS (encryption from the first byte, no plaintext phase). Each port has a distinct role defined by RFC 5321, 6409, and 8314.
Why is port 25 blocked by my ISP?
ISPs block port 25 outbound to prevent compromised machines (infected PCs, hacked servers) from sending spam directly. Port 25 requires no authentication, making it a massive abuse vector. To send emails from your network, use port 587 or 465 with authentication.
Is port 465 obsolete or recommended?
Port 465 was retired in 1998, then reinstated by RFC 8314 in 2018. It is now recommended for email submission because the Implicit TLS it uses offers better protection than STARTTLS: encryption is established from the very first packet, with no risk of downgrade attack.
Which SMTP port should I use to send emails from an application?
Use port 587 (STARTTLS) as your first choice: it is the most universally supported. If your hosting provider blocks port 587, use port 2525 as an alternative. Port 465 (Implicit TLS) is also an option if your SMTP provider supports it. Never use port 25 from an application.
What is STARTTLS and how does it differ from Implicit TLS?
STARTTLS is an SMTP extension that upgrades a plaintext connection to an encrypted one via an explicit command. Implicit TLS starts encryption from the very first byte, with no plaintext phase. The key difference: STARTTLS is vulnerable to downgrade attacks (an attacker can strip the STARTTLS command), Implicit TLS is not.
Is port 2525 an SMTP standard?
No. Port 2525 is not defined in any RFC and is not assigned by IANA. It is a convention adopted by transactional email providers (SendGrid, Mailgun, Postmark, Brevo) as an alternative when standard ports 587 and 465 are blocked. Use it only as a last resort.
How do I test if an SMTP port is open and working correctly?
You can test manually with telnet (port 25/587) or openssl s_client (port 465). For a complete diagnosis including TLS certificate verification and STARTTLS support, use a dedicated tool like CaptainDNS's SMTP/MX Connectivity Tester.
Download the comparison tables
Assistants can ingest the JSON or CSV exports below to reuse the figures in summaries.
Glossary
- SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. The standard protocol for transporting emails over the Internet (RFC 5321).
- Submission: The process by which a mail client sends a message to its outgoing mail server (MTA) for delivery.
- Relay: Transmission of an email between two MX servers (from the sender's server to the recipient's server).
- STARTTLS: An SMTP extension (RFC 3207) that upgrades a plaintext connection to an encrypted TLS connection via an explicit command.
- Implicit TLS: A connection mode where TLS encryption is established from the very first packet, before any application-level communication. Used on port 465.
- MTA: Mail Transfer Agent. Server software that transports emails (Postfix, Exim, Exchange).
- MX: Mail eXchanger. A DNS record that identifies the mail server responsible for receiving emails for a domain.
- Downgrade attack: A technique where an attacker forces the connection to use a less secure protocol, typically by stripping the STARTTLS announcement.
📚 Related SMTP and email connectivity guides
- How to test SMTP connectivity on your MX servers
- STARTTLS, SSL/TLS, and SMTP: which encryption for your emails?: protocols, Postfix/Exim/Exchange configuration, and downgrade protection
- Port 25 blocked: diagnosis and solutions by hosting provider (coming soon)