How to test the SMTP connectivity of your MX servers
By CaptainDNS
Published on February 17, 2026
- A valid MX record doesn't prove your mail server is working: test the TCP connection, banner, STARTTLS and TLS certificate
- Use
telnetto verify port 25 connectivity and the SMTP banner, thenopenssl s_clientto inspect STARTTLS and the certificate - Common issues (port 25 blocked, expired certificate, misconfigured STARTTLS) are silent: only active testing detects them
- Automate diagnostics with CaptainDNS's SMTP/MX Connectivity Tester to check all your MX servers in a single request
Your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records are properly configured. Your domain passes all DNS tests. Yet some emails don't reach their destination, or arrive without TLS encryption. The problem isn't DNS configuration, but the transport layer: the SMTP connection between servers.
This guide shows you how to test SMTP connectivity of your MX servers, from DNS resolution through TLS certificate inspection. Every command is reproducible from a Linux, macOS, or WSL terminal. Whether you're diagnosing a delivery issue or auditing the security of your email infrastructure, you'll know exactly what to check and how to interpret the results.
Why test SMTP connectivity of your MX servers?
DNS configuration (MX, SPF, DKIM, DMARC records) is a necessary condition, but not a sufficient one. Three categories of problems escape conventional DNS verification tools.
Deliverability depends on transport
If your MX server is unreachable on port 25, sending servers get a "connection timed out" error and retry for 24 to 48 hours before giving up. The message is lost, and the sender receives a late bounce. This type of outage is invisible from your side unless you actively test.
TLS encryption isn't guaranteed
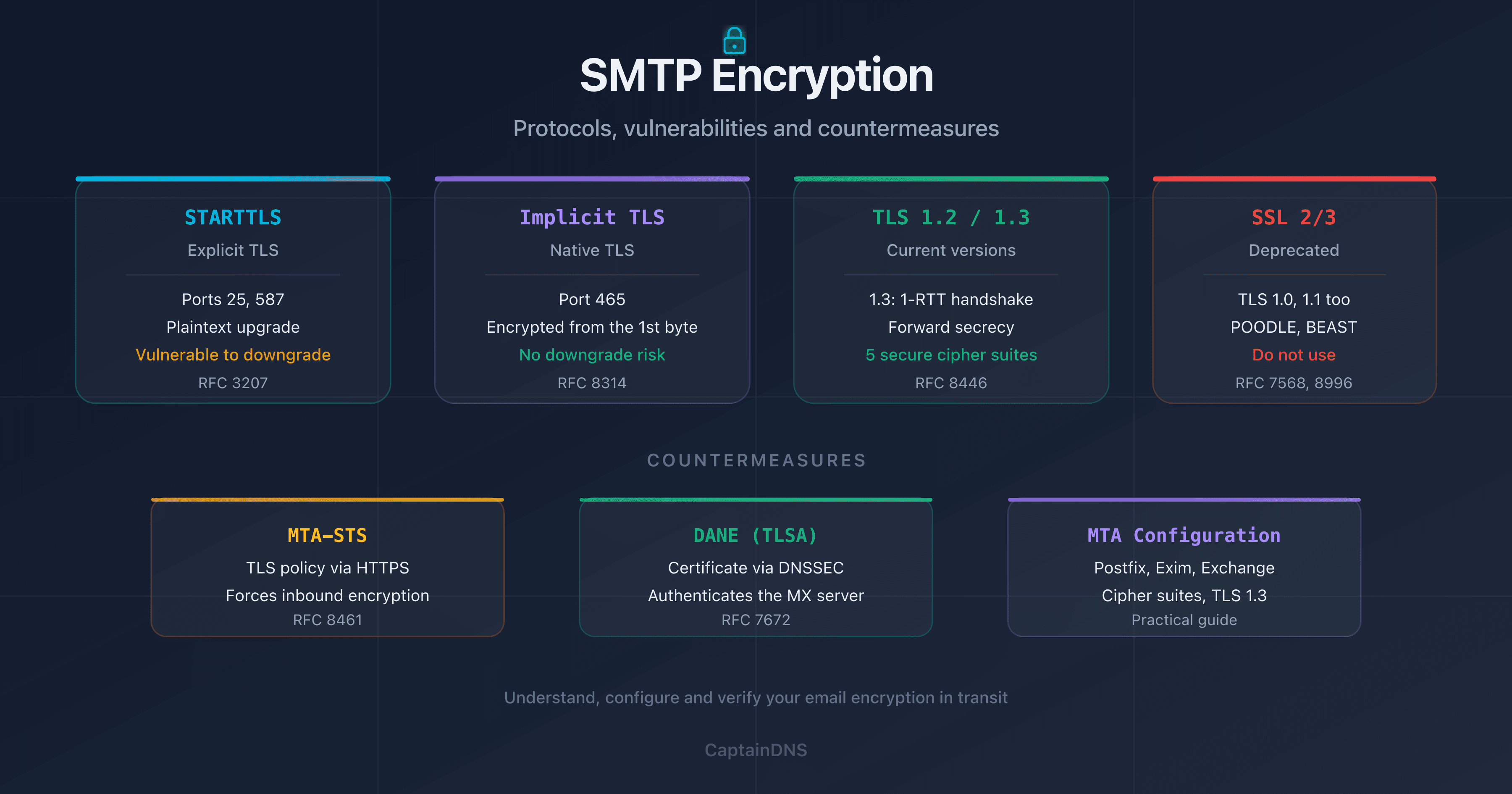
In 2024, over 95% of emails received by Gmail transit via TLS (Google Transparency Report). But STARTTLS is opportunistic: if the negotiation fails silently, the connection continues in plaintext. An expired certificate or misconfigured TLS can degrade the security of all your inbound traffic without triggering any alert.
An open relay destroys your reputation
An SMTP server that accepts to relay mail for anyone is an open relay. Spammers exploit it within hours, and your IP ends up on blacklists (Spamhaus, Barracuda, SpamCop). All your outbound emails are then rejected.
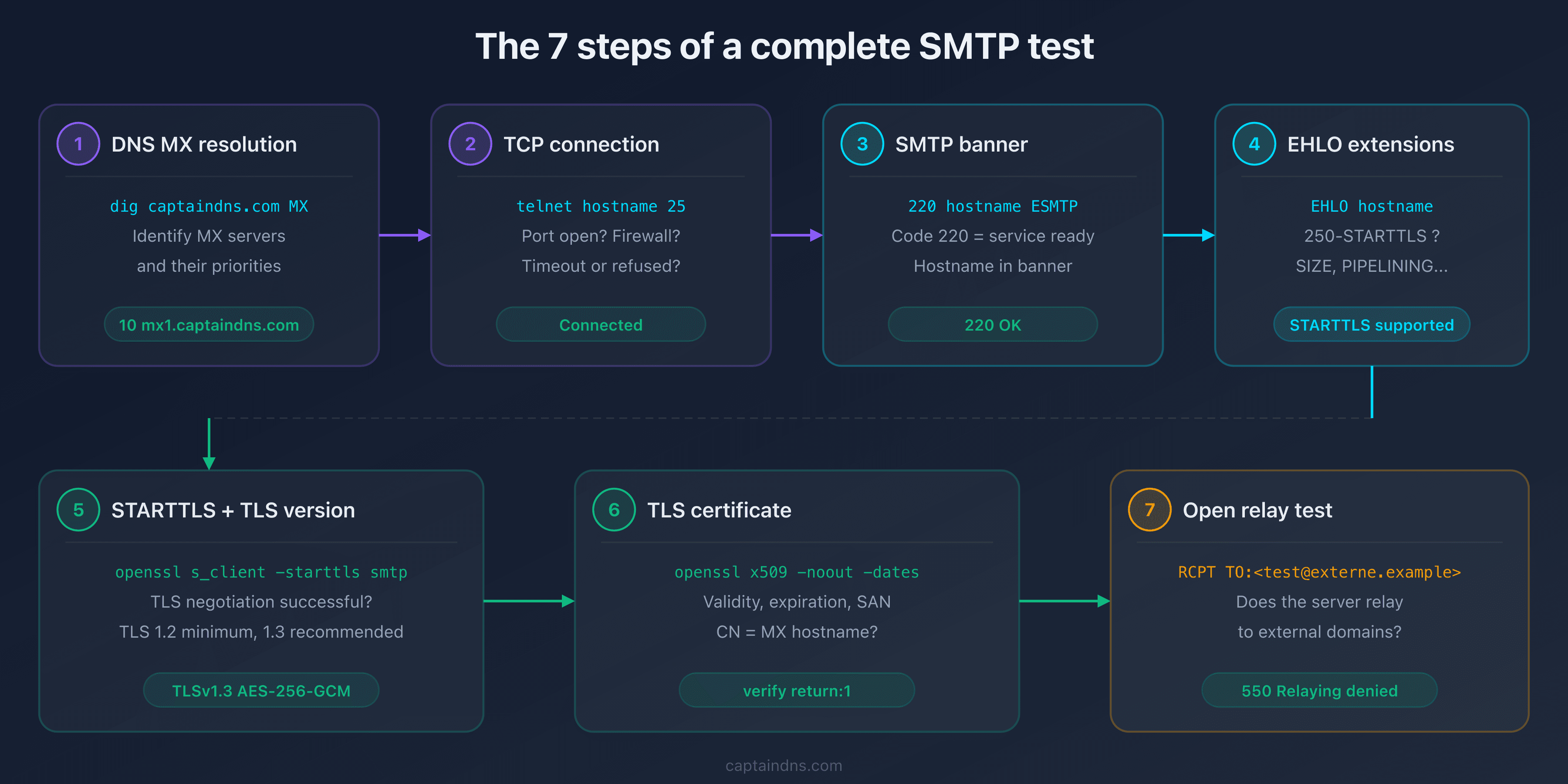
What a complete SMTP test checks
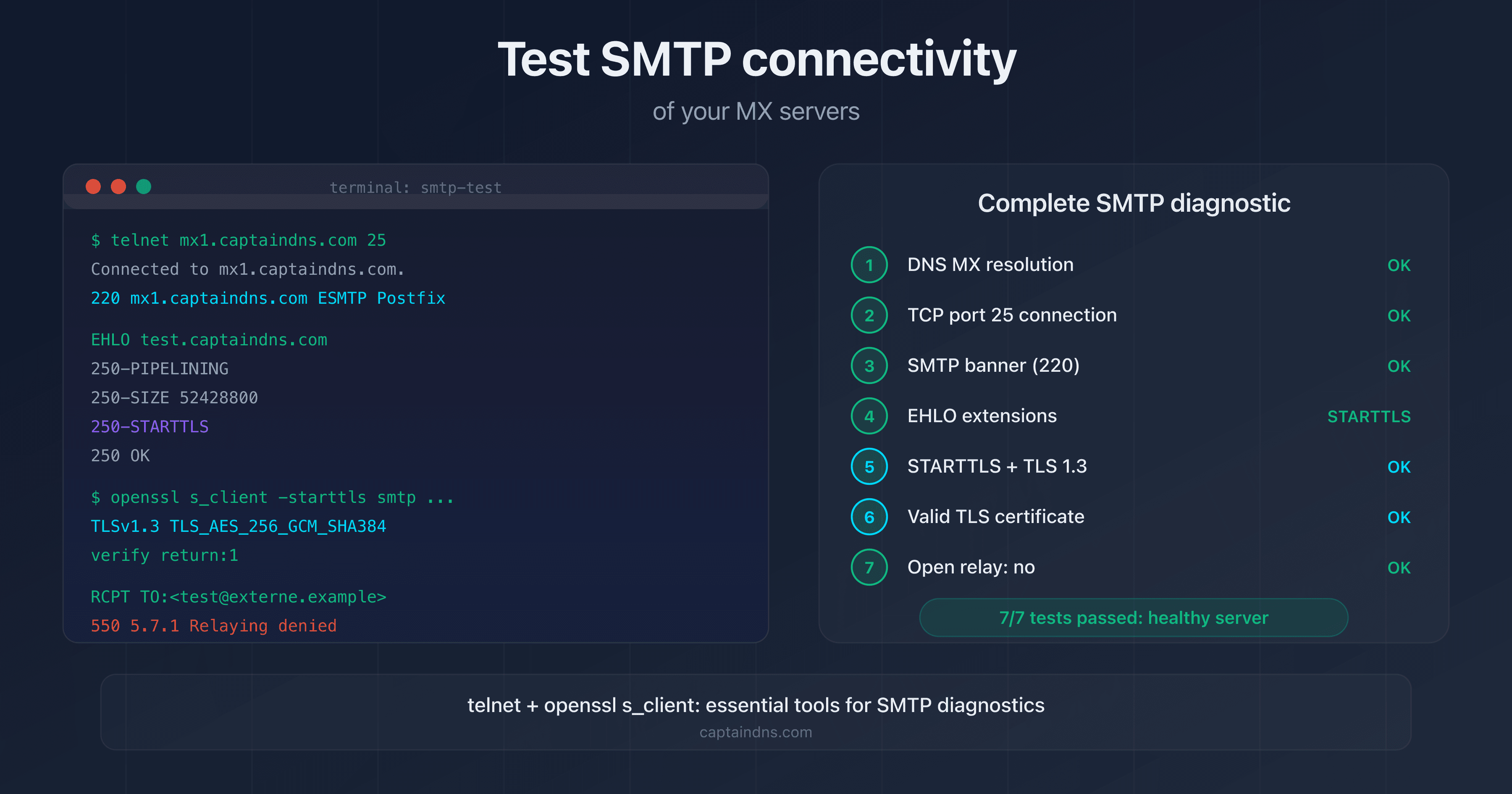
A complete SMTP connectivity test covers seven points, in this order.
| Step | Check | Tool |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | DNS MX resolution | dig or nslookup |
| 2 | TCP port 25 connection | telnet |
| 3 | SMTP banner (220) | telnet |
| 4 | EHLO extensions | telnet |
| 5 | STARTTLS and TLS version | openssl s_client |
| 6 | TLS certificate (validity, expiration, SAN) | openssl s_client |
| 7 | Open relay test | telnet |
Each step can fail independently. A server might respond on port 25, advertise STARTTLS in EHLO, but fail TLS negotiation because of an expired certificate.
Step 1: resolve MX records
Before testing connectivity, identify the MX servers for your domain. The dig command returns MX records sorted by priority:
$ dig captaindns.com MX +short
10 mx1.captaindns.com.
20 mx2.captaindns.com.
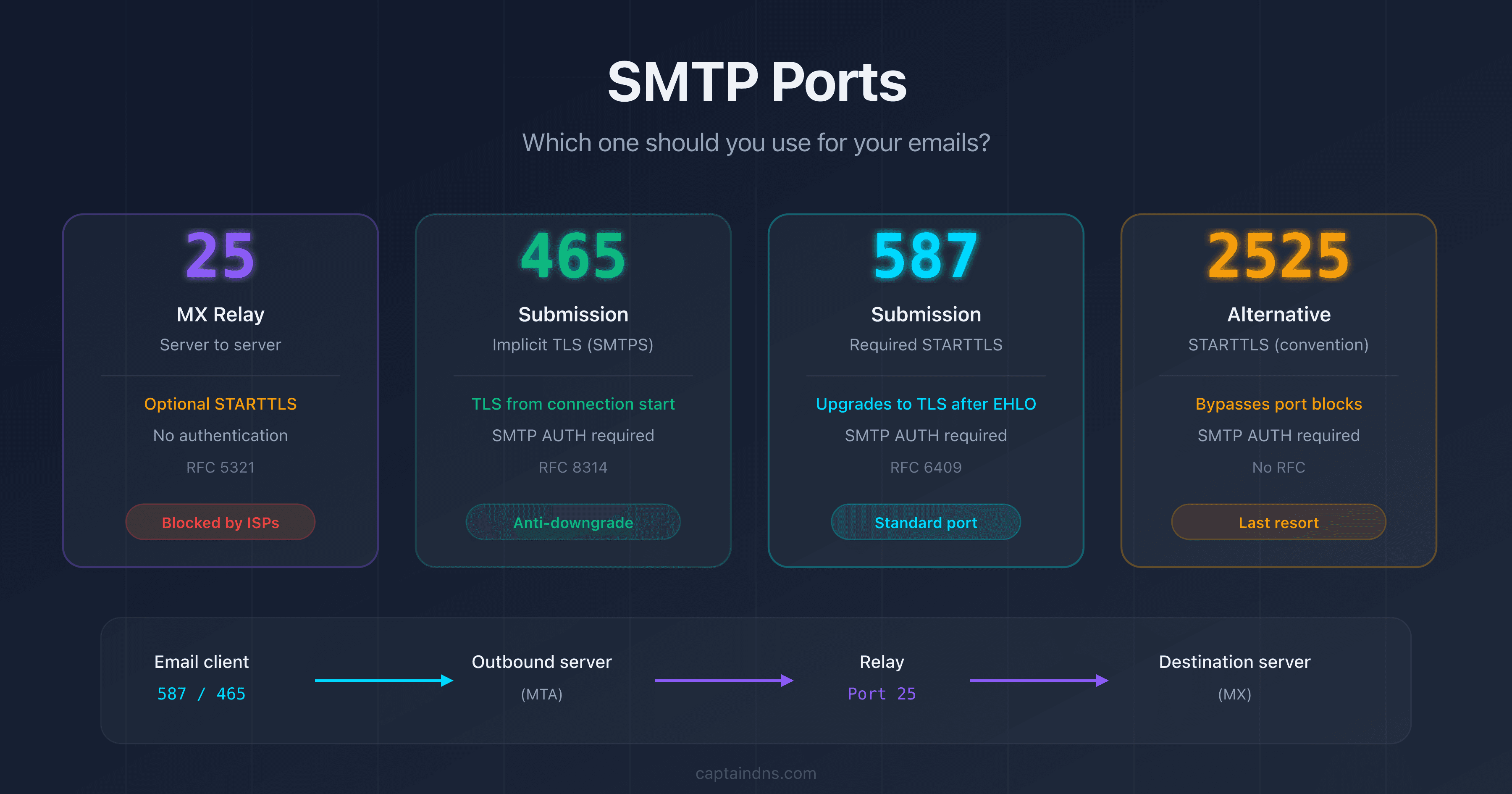
The number (10, 20) is the priority: sending servers contact the MX with the lowest value first. Test all your MX servers, not just the primary. A misconfigured secondary MX is still reachable and may accept mail without TLS.
If dig returns no results, the problem is DNS: your domain has no MX record, or the DNS isn't responding.
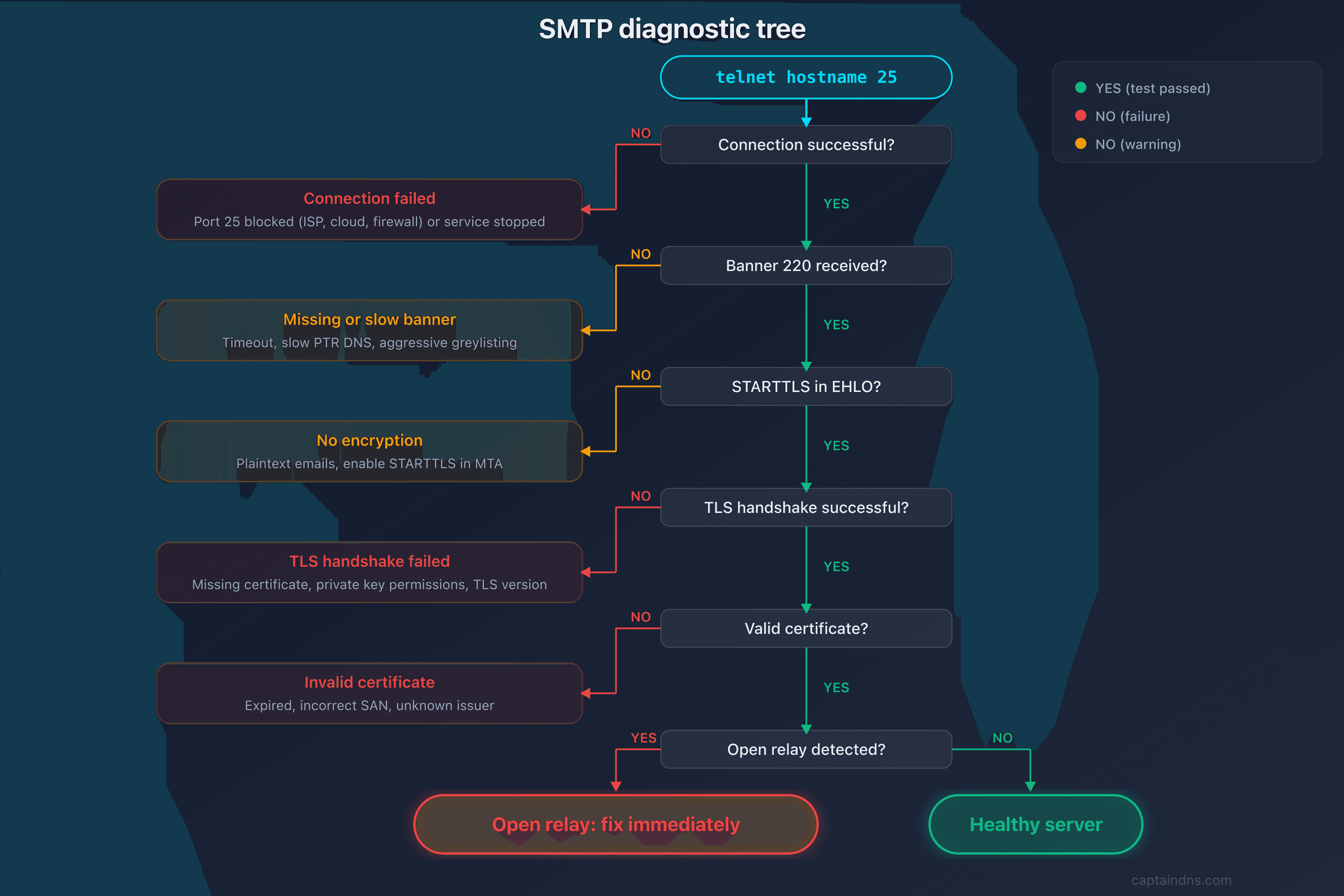
Step 2: test the TCP connection and banner with telnet
The telnet command tests two things in a single operation: opening TCP port 25 and receiving the SMTP banner.
$ telnet mx1.captaindns.com 25
Trying 203.0.113.10...
Connected to mx1.captaindns.com.
Escape character is '^]'.
220 mx1.captaindns.com ESMTP Postfix
Interpreting the result
| Result | Meaning | Action |
|---|---|---|
Connected + 220 ... | Server reachable, banner OK | Continue the test |
Connection refused | Port 25 closed or service stopped | Check the firewall and SMTP service |
Connection timed out | Port 25 blocked (ISP, firewall) | Test from a different network |
220 without hostname | Misconfigured banner | Fix the MTA config |
Capture EHLO extensions
After the banner, send the EHLO command to discover the server's capabilities:
EHLO test.captaindns.com
250-mx1.captaindns.com
250-PIPELINING
250-SIZE 52428800
250-STARTTLS
250-8BITMIME
250-SMTPUTF8
250 OK
Look for 250-STARTTLS in the response: this line confirms the server supports TLS encryption. If it's missing, the server only accepts plaintext connections.
Step 3: test STARTTLS and the TLS certificate with openssl
telnet can't initiate a TLS negotiation. To test STARTTLS and inspect the certificate, use openssl s_client:
$ openssl s_client -connect mx1.captaindns.com:25 -starttls smtp
CONNECTED(00000003)
depth=2 C = US, O = Internet Security Research Group, CN = ISRG Root X1
verify return:1
depth=1 C = US, O = Let's Encrypt, CN = R3
verify return:1
depth=0 CN = mx1.captaindns.com
verify return:1
---
Certificate chain
0 s:CN = mx1.captaindns.com
i:C = US, O = Let's Encrypt, CN = R3
1 s:C = US, O = Let's Encrypt, CN = R3
i:C = US, O = Internet Security Research Group, CN = ISRG Root X1
---
[...]
New, TLSv1.3, Cipher is TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
[...]
Key information to verify
TLS version: look for the line New, TLSv1.X. TLS 1.3 is optimal, TLS 1.2 is acceptable. TLS 1.0 and 1.1 are deprecated and vulnerable.
Certificate chain: verify return:1 at each level means the chain is valid. verify return:0 indicates a problem (expired certificate, unknown issuer, missing SAN).
Certificate subject: the CN or SANs must match the MX hostname. A certificate issued for mail.captaindns.com won't be valid for mx1.captaindns.com.
Check the expiration date
$ openssl s_client -connect mx1.captaindns.com:25 -starttls smtp 2>/dev/null | openssl x509 -noout -dates
notBefore=Jan 15 00:00:00 2026 GMT
notAfter=Apr 15 23:59:59 2026 GMT
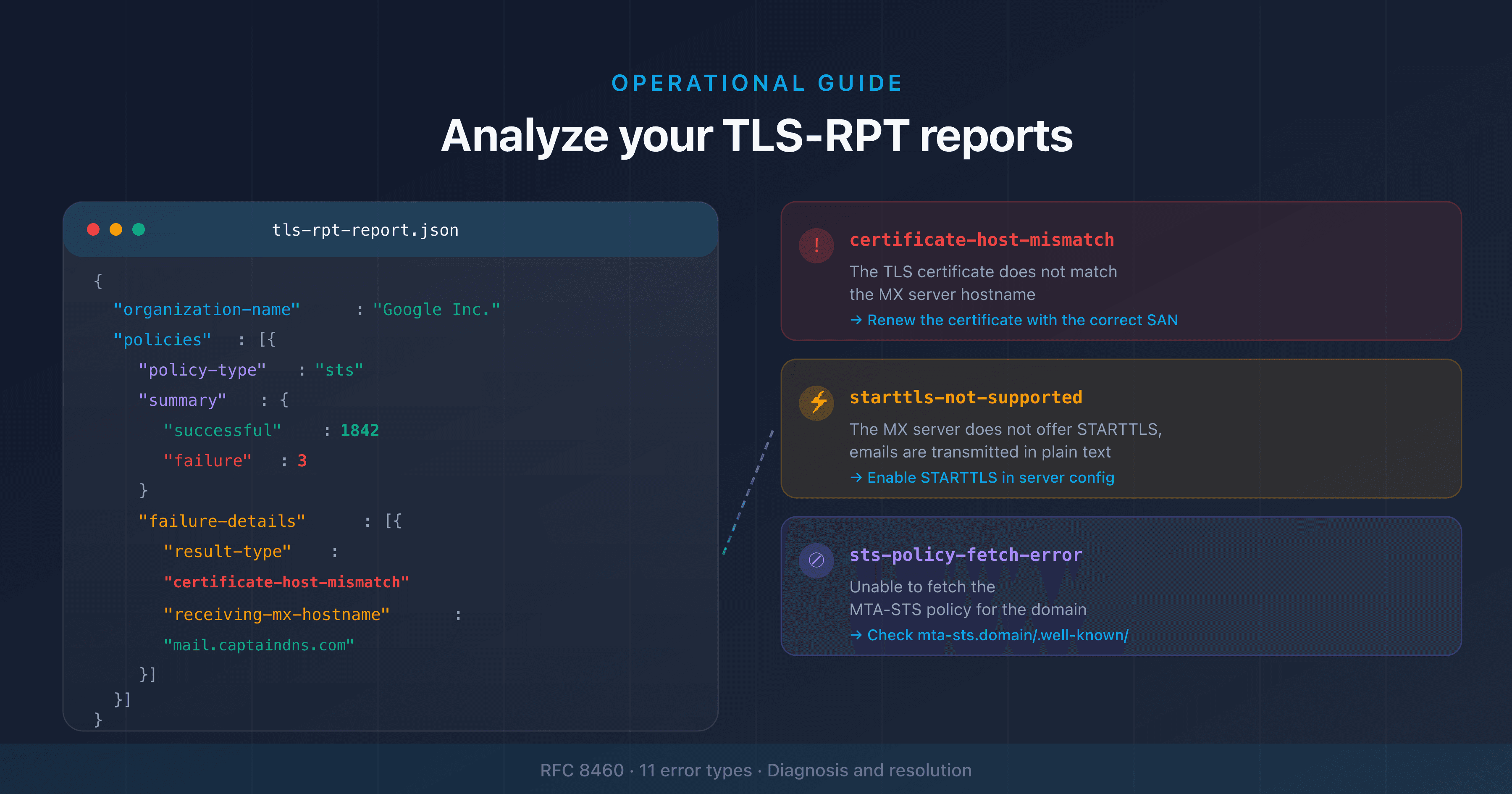
If notAfter is in the past, the certificate has expired. Sending servers that verify certificates (via MTA-STS or DANE) will refuse the connection.
Step 4: test for open relay
An open relay accepts to forward mail to external recipients without authentication. To detect it, try sending an email to a domain your server doesn't handle:
$ telnet mx1.captaindns.com 25
220 mx1.captaindns.com ESMTP
EHLO test.captaindns.com
250 OK
MAIL FROM:<test@captaindns.com>
250 OK
RCPT TO:<test@domaine-externe.example>
550 5.7.1 Relaying denied
QUIT
Interpreting the result
| RCPT TO response | Meaning |
|---|---|
550 Relaying denied | Server properly configured (not an open relay) |
250 OK | Open relay detected, urgent fix required |
450 or 451 | Active greylisting (normal, not an open relay) |
554 | Rejected for another reason (blacklist, policy) |
If your server returns 250 OK to a RCPT TO for an external domain, it's configured as an open relay. Fix your MTA configuration immediately (Postfix: smtpd_relay_restrictions, Exchange: receive connectors).
Diagnosing common issues
Port 25 blocked
Symptom: telnet mx1.captaindns.com 25 returns "Connection timed out".
Possible causes:
- Local or network firewall blocking outbound port 25
- Cloud provider (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure) blocking port 25 by default
- ISP blocking port 25 on residential connections
Diagnosis: test from a server outside your network. If the test passes from the outside but fails locally, the block is on the network/ISP side. For more details on port 25 blocking, see our guide on SMTP ports.
Expired TLS certificate
Symptom: openssl s_client shows verify return:0 and certificate has expired.
Impact: servers enforcing MTA-STS will refuse to deliver emails. Servers without MTA-STS will still deliver (opportunistic STARTTLS), but the connection isn't authenticated.
Solution: renew the certificate (Let's Encrypt: certbot renew), then reload the SMTP service.
STARTTLS advertised but fails
Symptom: the server advertises 250-STARTTLS in EHLO, but openssl s_client -starttls smtp fails with a handshake error.
Possible causes:
- Certificate referenced in MTA config but file missing or unreadable
- Incorrect permissions on private key files
- TLS version too old (TLS 1.0 rejected by client)
Diagnosis:
$ openssl s_client -connect mx1.captaindns.com:25 -starttls smtp -debug 2>&1 | head -30
Connection timeout (slow server)
Symptom: the TCP connection establishes, but the banner takes over 30 seconds to appear.
Impact: some sending servers give up after a timeout (generally 5 minutes for the banner, RFC 5321 section 4.5.3.2). A slow MX causes delivery delays and unnecessary retries.
Solution: check server load, aggressive greylisting rules, or slow reverse DNS lookups (PTR) in the MTA configuration.
Automating SMTP tests
The telnet and openssl commands are useful for one-off diagnostics, but they have limitations: they only test one server at a time, don't produce structured reports, and aren't practical for regular monitoring.
Quick verification bash script
#!/bin/bash
# Basic SMTP test for all MX servers of a domain
DOMAIN="captaindns.com"
echo "=== MX for $DOMAIN ==="
dig $DOMAIN MX +short | sort -n | while read priority mx; do
mx="${mx%.}" # Remove trailing dot
echo ""
echo "--- $mx (priority $priority) ---"
# Test port 25 connection
timeout 10 bash -c "echo QUIT | telnet $mx 25 2>&1" | head -5
# Test STARTTLS + certificate
echo | timeout 10 openssl s_client -connect $mx:25 -starttls smtp 2>/dev/null | \
openssl x509 -noout -subject -dates 2>/dev/null || echo "STARTTLS: failed or not supported"
done
This script tests each MX server for the domain: TCP connection, banner and TLS certificate. It doesn't cover the open relay test (which requires more complex SMTP interaction).
CaptainDNS online tool
For a complete diagnostic without installation, CaptainDNS's SMTP/MX Connectivity Tester automatically tests all MX servers of a domain in a single request: DNS resolution, port 25 connection, banner, EHLO, STARTTLS, TLS certificate and open relay detection. Results are presented with per-server scoring and explicit diagnostic codes.
Test the SMTP connectivity of your MX servers: Use our SMTP/MX Connectivity Tester to diagnose all your MX servers in seconds, with TLS certificate validation and open relay detection.
FAQ
How do I test if an SMTP server responds on port 25?
Use the command telnet hostname 25. If the connection establishes and you receive a line starting with 220, the server is reachable and the SMTP service is running. If you get "Connection refused" or "Connection timed out", the port is closed or blocked.
How do I check if an MX server supports STARTTLS?
Connect with telnet hostname 25, send EHLO your.hostname, and look for 250-STARTTLS in the response. To test the actual TLS negotiation, use openssl s_client -connect hostname:25 -starttls smtp. If the negotiation succeeds, STARTTLS is functional.
How do I inspect an SMTP TLS certificate with openssl?
Run openssl s_client -connect hostname:25 -starttls smtp 2>/dev/null | openssl x509 -noout -text. This command displays the subject, issuer, validity dates, SANs (Subject Alternative Names) and key type. Verify that the CN or a SAN matches the MX hostname.
How do I detect if a server is an open relay?
Connect to the server, send MAIL FROM:<test@captaindns.com>, then RCPT TO:<test@domaine-externe.example>. If the server returns 250 OK to the RCPT TO for a domain it doesn't handle, it's an open relay. A properly configured server returns 550 Relaying denied.
Why is my MX server unreachable on port 25?
The most common causes: firewall blocking port 25, cloud provider blocking port 25 by default (AWS, GCP, Azure), SMTP service stopped, or MX record pointing to the wrong IP. Test from a different network to isolate the cause.
What TLS version is acceptable for an MX server?
TLS 1.2 is the minimum acceptable in 2026. TLS 1.3 is recommended for optimal security and better performance (faster handshake). TLS 1.0 and 1.1 are deprecated (RFC 8996) and should no longer be enabled.
What online tools test SMTP connectivity?
CaptainDNS's SMTP/MX Connectivity Tester automatically tests all MX servers of a domain: banner, EHLO, STARTTLS, TLS certificate and open relay. Other tools like MXToolbox SMTP Test or CheckTLS offer similar features, but with less detail on the certificate.
Glossary
- SMTP banner: The server's first response (code 220) upon TCP connection. Contains the hostname and sometimes the MTA software (Postfix, Exchange, Exim).
- EHLO: Extended HELO. SMTP command that identifies the client and asks the server to list its extensions (STARTTLS, SIZE, PIPELINING, etc.).
- STARTTLS: SMTP extension (RFC 3207) that upgrades a plaintext connection to an encrypted TLS connection via an explicit command.
- Open relay: An SMTP server that accepts to forward mail to external recipients without authentication. A spam vector that causes rapid blacklisting.
- SAN: Subject Alternative Name. A TLS certificate field that lists the hostnames for which the certificate is valid.
- MTA: Mail Transfer Agent. Server software that transports emails (Postfix, Exim, Exchange, Sendmail).
- Greylisting: An anti-spam technique that temporarily rejects (code 450) emails from unknown senders. Legitimate servers retry, spammers don't.
📚 Related SMTP and email connectivity guides
- SMTP ports explained: 25, 465, 587, 2525: role, encryption, and use cases of each SMTP port
- STARTTLS, SSL/TLS, and SMTP: which encryption for your emails?: protocols, Postfix/Exim/Exchange configuration, and downgrade protection
- Port 25 blocked: diagnosis and solutions by hosting provider (coming soon)