Phishing trends 2025-2026: APWG statistics and new techniques
By CaptainDNS
Published on February 16, 2026
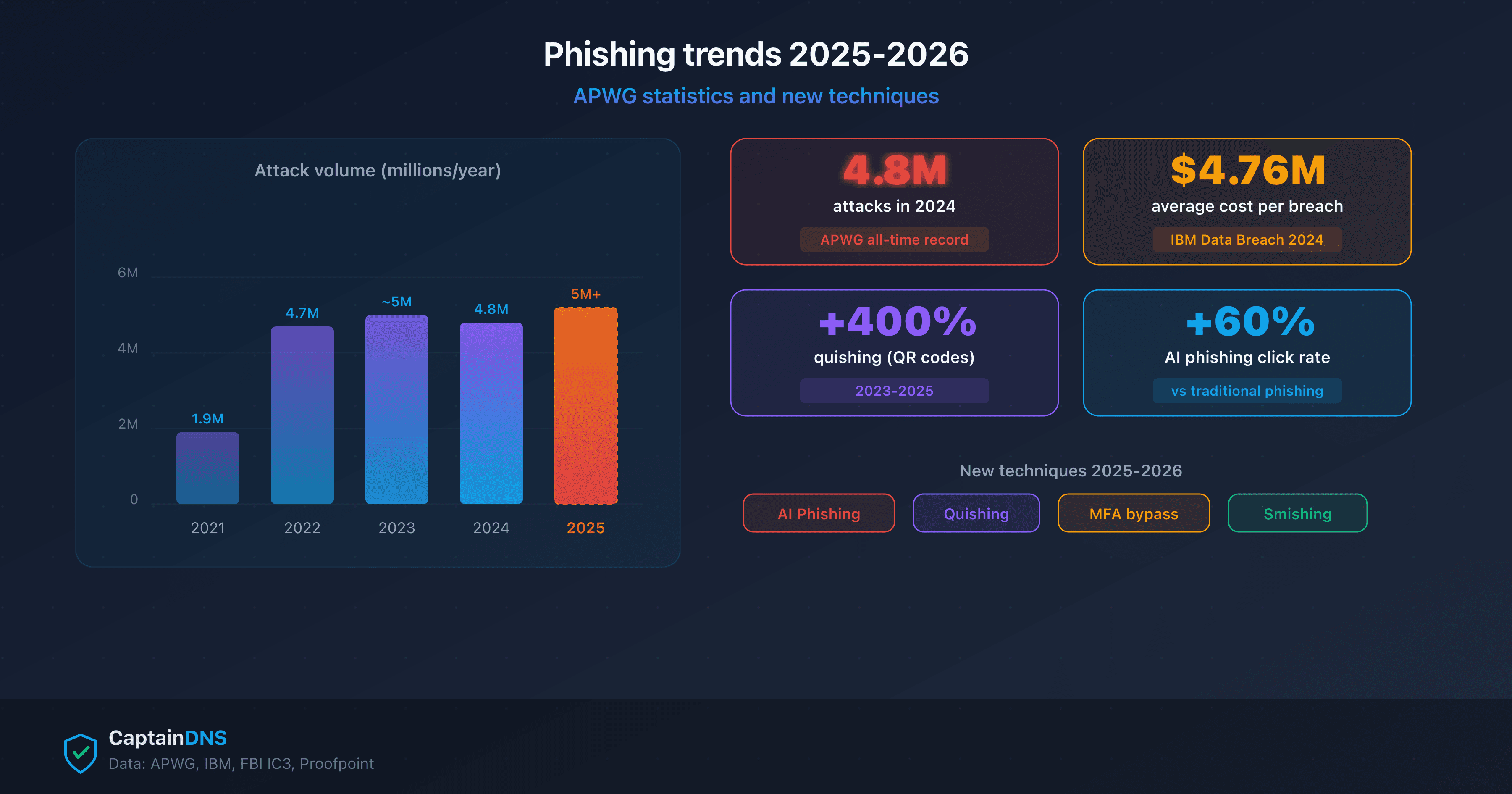
- The APWG recorded over 4.8 million phishing attacks in 2024, an all-time record up 20% from 2023
- Financial services and SaaS platforms account for 60% of phishing attacks
- AI-assisted phishing produces typo-free emails, making human detection much harder
- Quishing (QR code phishing) surged 400% between 2023 and 2025
- Combining multiple threat intelligence databases has become essential to detect new forms of phishing
In 2024, phishing crossed a threshold. The Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG) recorded 4.8 million attacks, the highest level since the organization was founded in 2003. And 2025 confirms the trend: attackers are no longer content with sending poorly written emails with dubious links.
Generative AI, QR codes and multi-factor authentication (MFA) bypass have changed the game. This article breaks down the key phishing figures, the most targeted sectors and the techniques redefining the threat in 2026. You'll understand why traditional defenses are no longer enough and how to adapt your protection.
Key phishing figures for 2025
APWG data and major security reports paint a clear picture: phishing continues to grow in both volume and sophistication.
Attack volume
| Year | Recorded attacks (APWG) | Change |
|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 4.7 million | +150% vs 2021 |
| 2023 | ~5 million (estimate) | +6% |
| 2024 | 4.8 million (confirmed) | Stable |
| 2025 (projection) | 5+ million | +5-10% |
Volume remains at historically high levels. The slight stabilization in 2024 doesn't signal a retreat: attacks are more targeted and more effective, offsetting raw volume.
Click rate and average cost
- Average click rate on a phishing email: 3.4% (source: Proofpoint State of the Phish 2024)
- Average cost of a breach linked to phishing: $4.76 million (IBM Cost of a Data Breach 2024)
- Average detection time for a phishing compromise: 207 days
A 3.4% click rate means that out of 1,000 targeted employees, 34 will click the malicious link. A single click is all it takes to compromise an entire network.
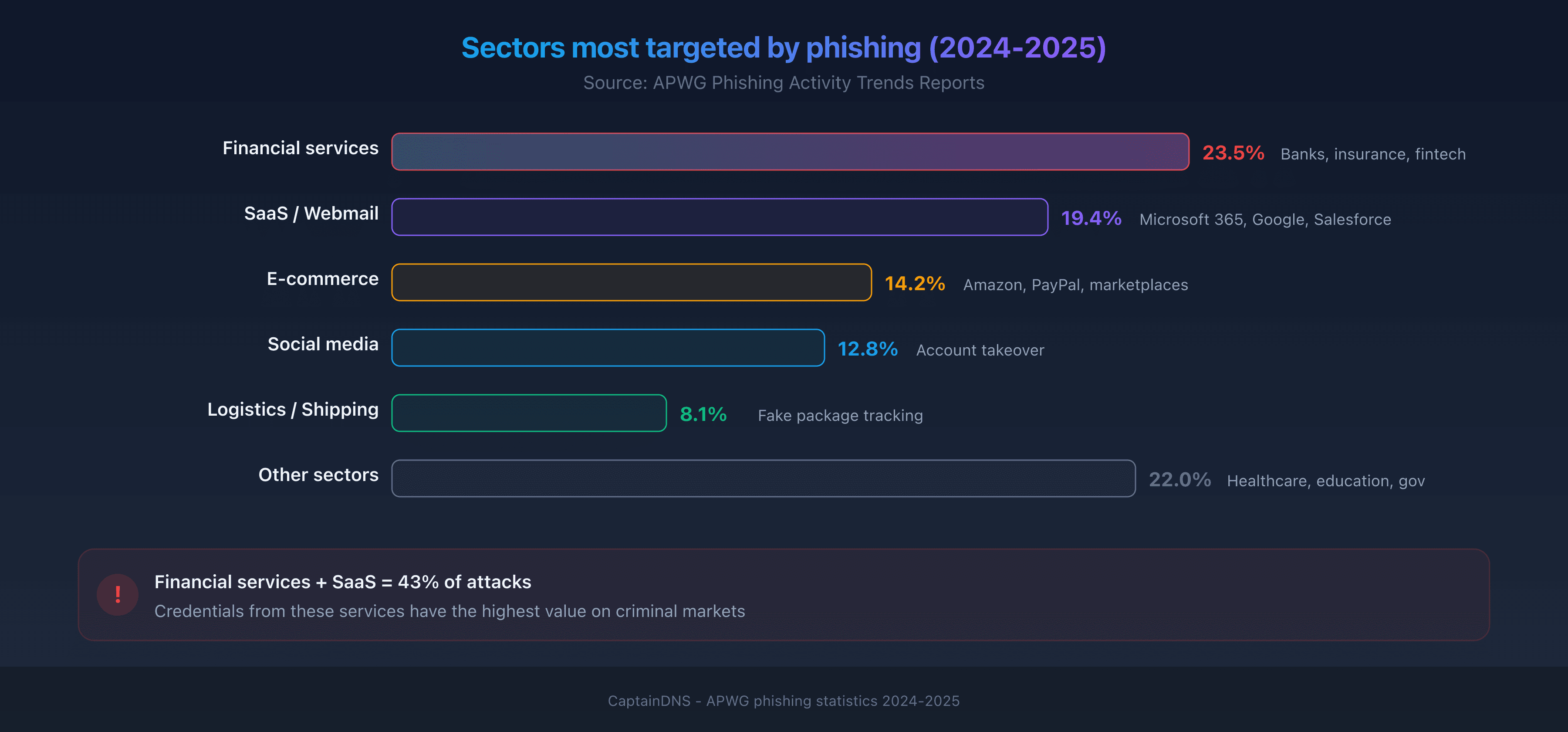
Most targeted sectors
The APWG identifies the most targeted sectors in its quarterly reports. In 2024-2025, the distribution remains concentrated.
Top 5 sectors
- Financial services (23.5%): banks, insurance, fintech. Banking login pages remain phishing's #1 target.
- SaaS and webmail (19.4%): Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, Salesforce. Stolen credentials grant access to entire ecosystems.
- E-commerce (14.2%): Amazon, PayPal and marketplaces. Fake delivery notices spike during sale periods.
- Social media (12.8%): account takeover to spread spam or scams.
- Logistics and shipping (8.1%): fake package tracking, a particularly effective vector.
Why these sectors?
Attackers target services where the victim has a quick-login reflex. An email saying "Your account has been locked" triggers an immediate reaction. Financial services and SaaS combine two factors: a large user base and high value of stolen credentials.
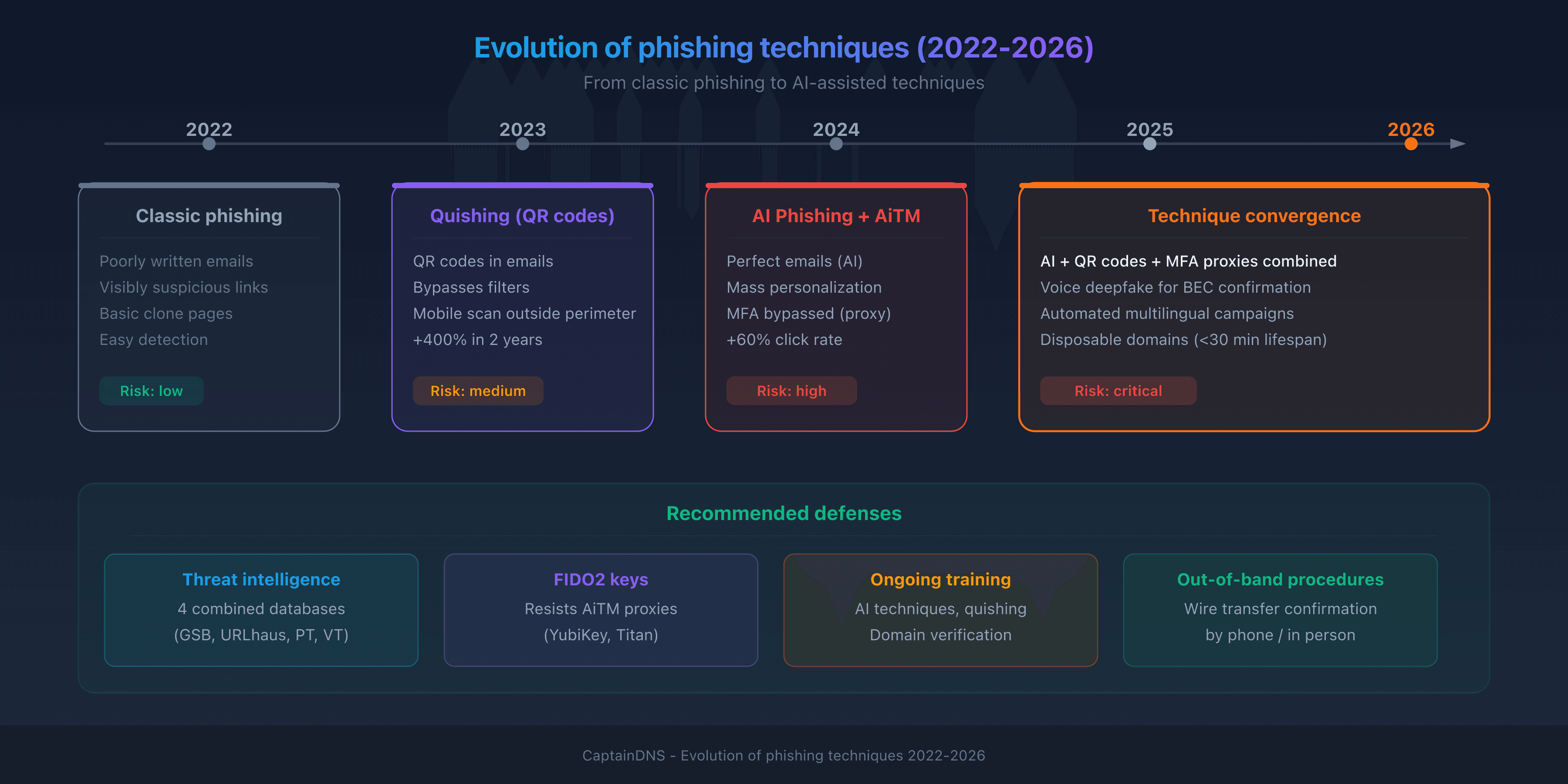
New phishing techniques in 2025-2026
Phishing evolves faster than defenses. Four techniques are redefining the threat.
AI-assisted phishing
Generative AI (ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini) enables producing phishing emails with no typos, in a professional and personalized style. According to a University of Oxford study (2024), AI-generated phishing emails have a 60% higher click rate than traditional ones.
What AI changes for attackers:
- Mass personalization: each email is tailored to the target (name, company, context)
- Native multilingual: campaigns in German, Japanese or Portuguese as convincing as those in English
- Clone site generation: AI can replicate a legitimate site in minutes
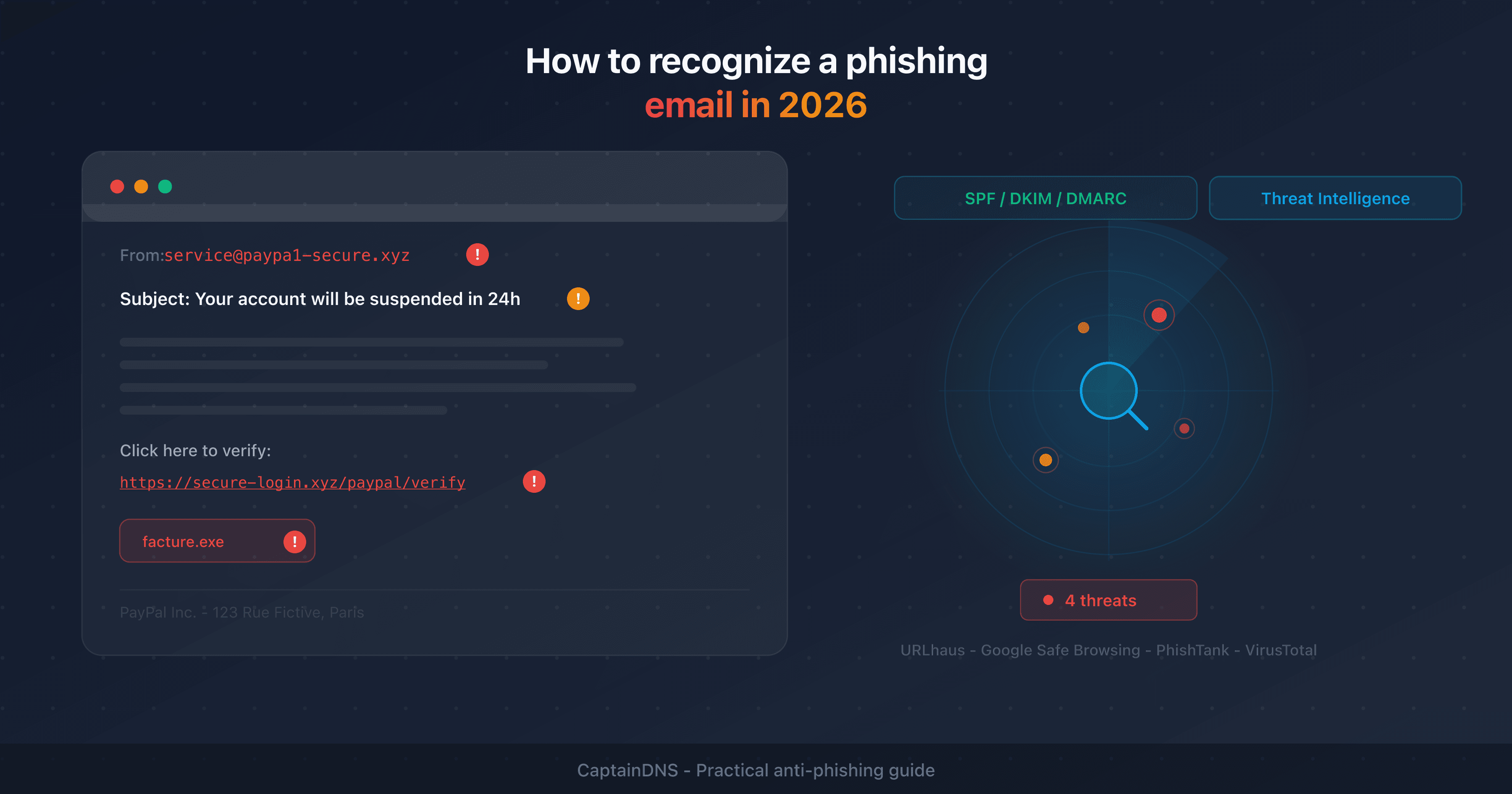
The "poorly written email = phishing" filter no longer works. Recognizing a phishing email now requires analyzing technical metadata (headers, sending domain) rather than visible content.
Quishing (QR code phishing)
Quishing uses QR codes to direct victims to malicious sites. This technique bypasses traditional email security filters because the malicious link is encoded in an image, not in text.
Why quishing is surging in 2025:
- QR codes became familiar during the pandemic (restaurants, transit, payments)
- Email filters don't scan images to extract URLs
- Scanning happens on mobile, often outside the corporate security perimeter
According to Abnormal Security, QR code attacks increased 400% between 2023 and 2025. The most affected sectors: energy, healthcare and manufacturing.
MFA bypass (adversary-in-the-middle)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) was considered an effective defense against phishing. Adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) attacks bypass this protection.
How an AiTM attack works:
- The victim clicks a phishing link
- The malicious site acts as a transparent proxy to the real site
- The victim enters their username, password and MFA code
- The proxy intercepts the authenticated session cookie
- The attacker uses that cookie to access the account without MFA
Frameworks like EvilGinx2 and Modlishka automate these attacks. Microsoft reported 10,000+ AiTM attacks per month targeting its users in 2024.
Mobile phishing (smishing)
Smishing (SMS phishing) exploits the trust placed in text messages and the small screen size of mobile devices, which hides full URLs.
Smishing trends in 2025:
- Messages impersonating banks, delivery services and tax authorities dominate
- The click rate on SMS links is 6 to 8 times higher than for emails
- Attacks use short codes (shortcodes) to appear legitimate
BEC (Business Email Compromise): the costliest form of phishing
BEC isn't mass phishing. It's a targeted attack where the attacker impersonates an executive, vendor or partner to obtain a fraudulent wire transfer.
BEC figures
- Global losses: $2.9 billion in 2023 (FBI IC3)
- Average loss per incident: $125,000
- BEC share of cybercrime losses: 37% of the total (FBI)
BEC exploits trust and urgency, not technology. An email saying "Can you process this $85,000 wire before 5pm?" sent from the compromised CFO's account is nearly impossible to distinguish from a legitimate request.
BEC and AI
AI strengthens BEC by enabling:
- Voice cloning (audio deepfake) to confirm requests by phone
- Analysis of previous email exchanges to replicate the executive's writing style
- Automatic translation to target foreign subsidiaries
Why traditional defenses are no longer enough
Classic email filters rely on three pillars: blocklists, URL analysis and text pattern detection. Modern phishing bypasses all three.
| Defense | Bypass method |
|---|---|
| Blocklists (Safe Browsing, PhishTank) | Disposable URLs, fresh domains (<30 min lifespan) |
| Real-time URL analysis | QR codes (link inside an image) |
| Text pattern detection | Generative AI (flawless, personalized text) |
| MFA (SMS codes, TOTP) | AiTM proxies (session interception) |
| Attachment analysis | Files hosted on legitimate cloud services |
No single defense layer is enough. Effective protection combines multiple approaches: technical (multi-source threat intelligence), human (ongoing training) and procedural (wire transfer verification).
How to protect yourself effectively in 2026
1. Multiply your threat intelligence sources
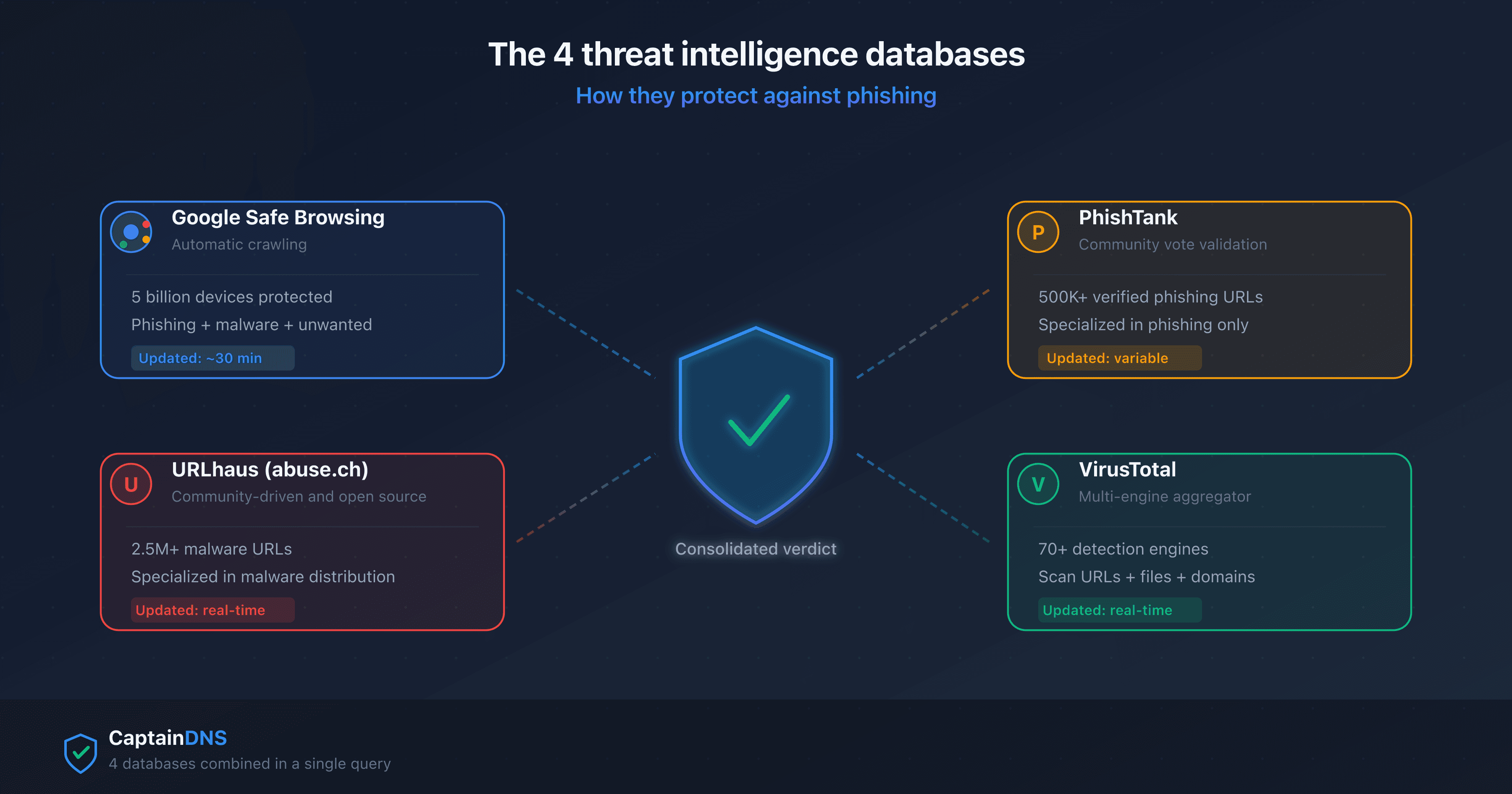
A single threat intelligence database misses 15 to 30% of threats. Combining Google Safe Browsing, URLhaus, PhishTank and VirusTotal reduces false negatives by cross-checking verdicts from independent sources.
2. Train users on new techniques
Traditional training ("spot the typos") is obsolete against AI phishing. Awareness programs must cover:
- Checking sender domains (not just the display name)
- Being wary of unsolicited QR codes
- Using out-of-band confirmation procedures for wire transfer requests
3. Adopt FIDO2 security keys
FIDO2 hardware keys (YubiKey, Titan) are the only effective protection against AiTM attacks. Unlike SMS or TOTP codes, FIDO2 keys are domain-bound: they refuse to authenticate on a proxy site that spoofs the legitimate domain.
4. Systematically check suspicious links
Before clicking a suspicious link, analyze it with a multi-database URL checker. A tool that queries 4 threat intelligence databases simultaneously detects more threats than a browser alone.
FAQ
How many phishing attacks are recorded per year?
The APWG recorded 4.8 million phishing attacks in 2024, a historically high level. In the 2025 projection, volume is expected to exceed 5 million. These figures only count reported attacks: the actual volume is estimated at 2 to 3 times higher.
What sector is most targeted by phishing?
Financial services (banks, insurance, fintech) account for 23.5% of phishing attacks according to the APWG, followed by SaaS and webmail platforms (19.4%). These two sectors represent over 40% of attacks because stolen credentials have high value.
How is AI changing phishing?
Generative AI enables producing typo-free, personalized and multilingual phishing emails. According to a University of Oxford study, AI-generated phishing emails have a 60% higher click rate than traditional emails. The "poorly written email = phishing" filter no longer works.
What is quishing?
Quishing is phishing via QR code. The attacker includes a QR code in an email, flyer or poster that redirects to a malicious site. This technique bypasses classic email filters because the malicious link is encoded in an image, not in text. Quishing attacks surged 400% between 2023 and 2025.
Does MFA still protect against phishing?
Classic MFA (SMS codes, TOTP apps) no longer protects against adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) attacks. These attacks intercept the session cookie after the victim completes MFA authentication. Only FIDO2 security keys resist AiTM attacks because they verify the site's domain.
What is BEC (Business Email Compromise)?
BEC is a targeted attack where the attacker impersonates an executive or vendor to obtain a fraudulent wire transfer. The FBI estimates global BEC losses at $2.9 billion in 2023. BEC exploits trust and urgency, not technical vulnerabilities.
How to detect an AI-generated phishing email?
Text content is no longer a reliable indicator. Instead, analyze technical metadata: check the actual sending domain (not the display name), verify DKIM and SPF headers, and run suspicious links through a multi-database URL checker. The combination of technical analysis and multi-source verification remains the most reliable method.
What are FIDO2 keys and why are they recommended?
FIDO2 keys (YubiKey, Google Titan) are hardware authentication devices that cryptographically verify the site's domain. Unlike SMS or TOTP codes, they refuse to authenticate on a proxy site that spoofs a legitimate domain. They are the only effective protection against adversary-in-the-middle attacks.
Glossary
- APWG (Anti-Phishing Working Group): international coalition of over 2,200 organizations that has been collecting and analyzing global phishing data since 2003.
- Quishing: phishing technique using QR codes to direct victims to malicious sites, bypassing traditional email filters.
- AiTM (Adversary-in-the-Middle): phishing attack where a proxy intercepts communications between the victim and the legitimate site, capturing the session cookie after MFA authentication.
- BEC (Business Email Compromise): targeted attack where the attacker impersonates an executive or partner to obtain a fraudulent wire transfer or sensitive data.
- FIDO2: hardware authentication standard based on asymmetric cryptography, resistant to phishing attacks because it is bound to the site's domain.
- Smishing: SMS phishing, exploiting the trust placed in text messages and the small screen size of mobile devices.
Check a suspicious link: use our phishing URL checker to query Google Safe Browsing, URLhaus, PhishTank and VirusTotal in a single request.
Related phishing guides
- How to recognize a phishing email in 2026
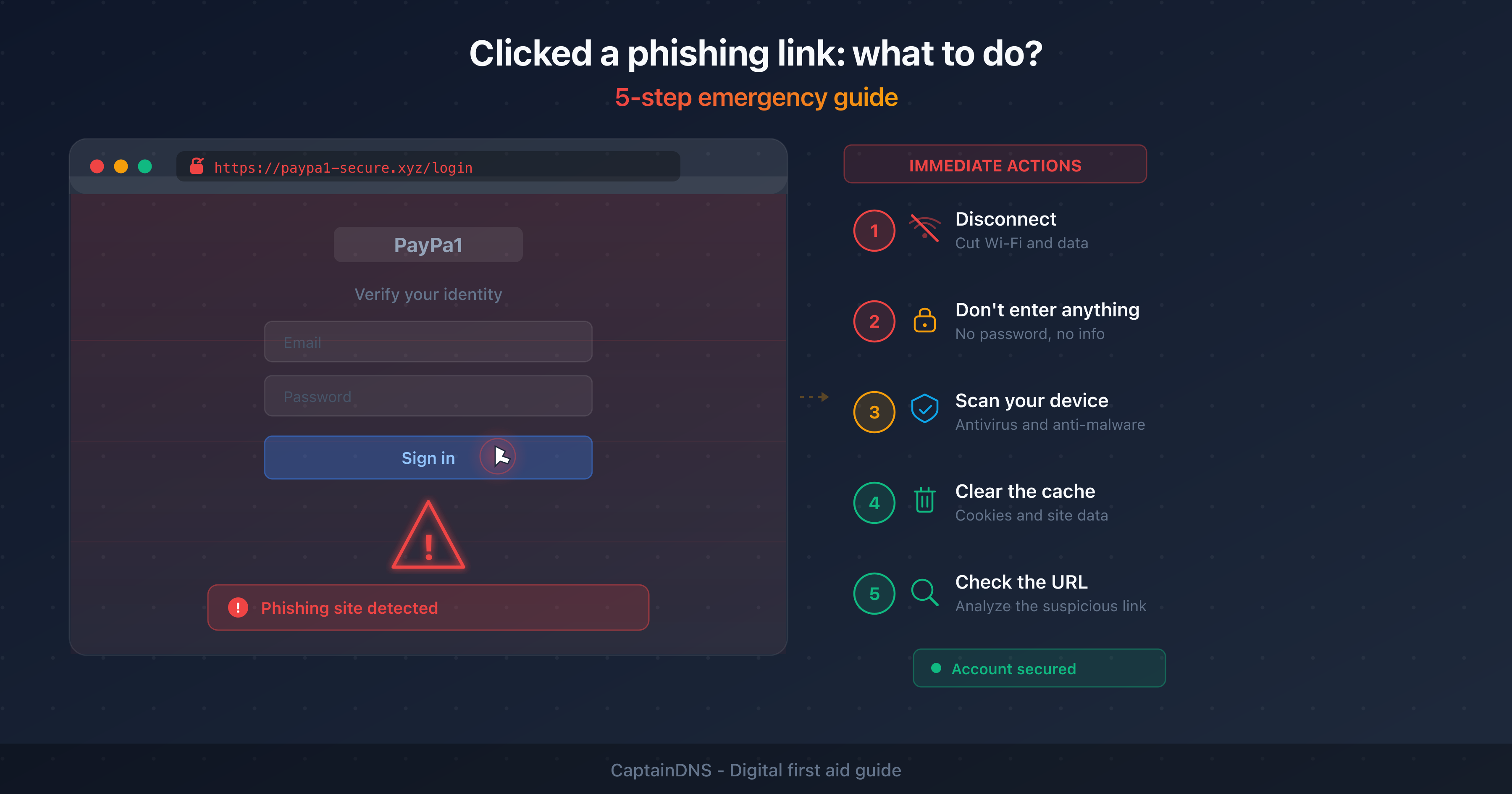
- What to do if you clicked a phishing link
- Google Safe Browsing, URLhaus, PhishTank, VirusTotal: how threat intelligence databases work